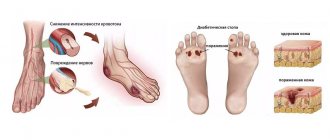
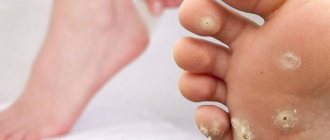
Reasons for the development of keratoma
The main reason for its occurrence is a violation of the influence of ultraviolet radiation on the epidermis, which occurs due to the aging of cells and the loss of their protective properties. The fact that in most cases older people are susceptible to this defect only confirms this fact. That is why this disease is also called “senile” and “age-related”.
However, prolonged exposure to the sun, even at a young age, can provoke keratinization of tissues. In this case, neoplasms appear in the most vulnerable places: on the hands, face, neck and décolleté.
At risk are people who abuse tanning, those with light and thin skin, as well as those who ignore the use of sunscreen.
The reasons for the deterioration of the skin condition and its resistance to external factors are:
- Lack of nutrients and vitamins in the diet;
- Abuse of animal fats and lack of vegetable fats, which are a source of vitamin E;
- Genetics - a tendency to a disease can be inherited;
- Tendency to oily seborrhea.
Important! Spots on the face and head can appear in older summer residents who do not cover their heads from the sun.
Types and symptoms of keratosis on the face
Keratosis on the face can be of several types, depending on the etiology and process of its development.
Actinic
– most often associated with prolonged exposure to UV radiation.
First, irregularities appear on the face, which progress to scaly patches
various shades (from skin color to red-brown). The sizes of formations may vary.
Seborrheic
- oval formations, which are characterized by slow growth. First, a spot of about 2-3 cm of a yellowish tint appears, which gradually thickens and becomes covered with greasy crusts. They can be easily separated from the skin.
Progressing
, the formation increases in diameter. The crusts layer on top of each other and darken. Moderate bleeding from the formation is possible due to the appearance of cracks.
Follicular - characterized by the formation of a node with clear boundaries of a pale flesh-colored or pink shade. The diameter of the formation is no more than 1.2 cm.
Its surface is slightly lumpy, with a depression or flat silvery scale in the center. Typically such a keratoma is observed on the cheeks, nasolabial fold or lip border.
Senile
– usually develops after 50 years. The first symptom is the appearance of a yellowish spot that resembles a highly pigmented patch of skin. Over time, the formation becomes darker and grows in diameter.
The structure of the keratoma becomes softer and looser. Later, roughness and flaking appear. Dimensions of education
can vary from 1/2 to 6 cm.
Varieties and symptoms
In medicine, there are several types of keratoma:
- Seborrheic - manifests itself as dark brown extensive spots, on the surface of which deep painful cracks form. The patient experiences severe itching, burning and peeling. Over time, parts of the keratomas may fall off, leaving open bleeding wounds that cause a lot of discomfort. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid infection in the tissue;
- Horny - in most cases it manifests itself as multiple heels in a variety of places and has cone-shaped spots that rise above the surface by 5-8 mm. This is the most dangerous type of disease with a high risk of developing a malignant tumor, so horny formations require immediate surgical removal;
- Senile – most often diagnosed in older people. Light gray spots are localized on the neck, face, back and stomach. Over time, they become denser and inflamed, forming painful lesions;
- Sunny – men and people with fair skin are more prone to this variety. It appears in places exposed to direct sunlight - forehead, head, collar area. This species is also dangerous for the development of tumors;
- Senile - the difference from other types is the large diameter of the plaques (up to 6 cm), slow development and temporary nature (they can disappear and reappear without treatment). At first, small formations may resemble moles or warts, but over time they begin to become cracked and begin to bleed;
- Follicular - gray-pinkish nodules with a diameter of 1-2 cm, more often found in women over 30 years old on the face, lips and under the hair. The rarest species.
We recommend reading: Psoriasis: causes, types and symptoms, treatment at home
The doctor explains what a keratoma is and how to treat this problem:
The course of the disease depends on its type and the person’s condition. There are several clinical stages of development with the following symptoms:
- a small inclusion of light brown color with a smooth surface;
- nodules and papules form that rise slightly above the surface of the skin;
- in place of the spots, keratomas appear directly, which outwardly resemble age-related convex dark-colored warts that begin to bleed upon tactile contact;
- extensive growth of warts in width and height, with severe keratinization of cells. a cone-shaped horn is formed.
In order to recognize the disease in time, it is necessary to pay attention to the signs that distinguish keratoma from moles and age spots - peeling, itching, rapid growth throughout the body and thickening.
Characteristics of the pathology
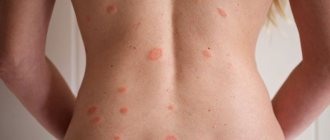
With age, skin particles cease to fully exfoliate, and the production of new epithelial cells decreases. This leads to the formation of a keratoma. Such formations are benign, but sometimes they can still become oncogenic (in 8-20% of situations). The pathology occurs on the face, neck, body, arms and upper legs.
At first, the neoplasm resembles a slightly protruding spot of a coffee or gray hue, then its area begins to grow, and a keratinized crust appears on the surface of the skin. If the area is touched, pain may occur and even bleeding may begin. Otherwise, the problem, as a rule, causes only aesthetic discomfort and practically does not bother the patient. There are several types of keratomas:
- Senile. This is a collection of neoplasms that can grow and increase. They usually have a dark brown tint, are prone to inflammation and are covered with a crust on top.
- Follicular. The neoplasm in the form of a nodule occurs in large numbers. This is the rarest form of pathology; the nodules are pink and appear above the lip.
- Seborrheic. It appears in the form of age spots, which over time begin to become darker and larger. They may also crack and cause itching. Occurs in the hairline area.
- Solar. The formations appear in large numbers and are covered with small scales.
- Horny. It can be of different shapes and localization. In some cases, it tends to become malignant.
Danger of keratoma
Keratoma is safe until the process of its degeneration begins and the tumor turns into cancer. Therefore, it is extremely important to monitor the condition of your skin and note changes. It is worth visiting a doctor if the patient notices that:
- the tumor began to grow rapidly;
- the affected area bleeds, although it was not injured;
- The keratoma is constantly itching.
In addition, there is another danger of such formations. Some types of skin cancer are visually very similar to keratoma, which is why even specialists cannot always distinguish one pathology from another. In such situations, it is necessary to remove the suspicious formation as soon as possible and send it for histological examination.
If histology shows that it is a cancerous tumor, the patient will need to undergo chemotherapy. Another danger is that when many keratomas appear on the skin at the same time, the likelihood of cancer in general increases.
Treatment methods at home
The first stage of treatment at home is compliance with preventive measures aimed at preventing and developing plaques. The sooner a set of measures is taken, the greater the chance of recovery. When you notice the first symptoms, you should:
- Completely avoid exposure to the sun or use protective equipment;
- Taking antioxidants and immunostimulants stops the appearance of spots: it is recommended to consume vitamin C in the form of ascorbic acid (5-6 tablets per day), or include citrus fruits, berries and kiwi in the menu.
- Taking multivitamin complexes and adding plenty of fruits and vegetables to your diet.
- Consuming natural sources of vitamin E: olive, sunflower and other vegetable oils, nuts and seeds.
- Correct sleep schedule.
- Elimination of stress and tension.
To reduce the inflammatory process and quickly heal wounds, it is recommended to regularly lubricate the affected areas with hormonal ointments, including flucinar and fluorocort. Moderate use of medicinal products helps to stop cell keratinization, the inflammatory process and relieve peeling.
Why you may need to remove a keratoma
Keratoma is a benign neoplasm on the skin, which consists of epidermal cells. It can be either small in size (a few millimeters) or quite large (up to 5 centimeters in diameter). Keratomas are usually slightly darker than the natural color of the skin or have a brown color. Over time, the surface of the keratoma becomes rough and rough.
The neoplasm is formed from human skin cells, which gradually layer on top of each other. At the same time, the upper layer becomes horny, skin scales die and fall off under mechanical stress, for example, during washing, but the deeper layers of the dermis also become keratinized. The process of continuous cell renewal leads to the fact that the keratoma does not disappear on its own, but can cause inconvenience for a long time.
Under normal conditions, the number of dead and new cells on human skin is balanced in such a way that the epidermis has time to renew itself in time and maintain a healthy state. If this balance is disturbed and the cells become keratinized at a faster rate than they are renewed, then various growths appear on the skin, including benign ones, such as keratomas.
Benign neoplasms on the skin are not dangerous to human health, since they consist of normal, unchanged cells. However, there is a fairly high probability that these formations will degenerate into malignant ones when exposed to a number of negative factors. These include, for example, excessive sun exposure or contact with toxic chemicals.
Keratomas can occur on any area of the skin. They can be single or form groups. Most often, keratomas are located on the neck, shoulders and arms. Less common on the lower body.
Currently, the reasons for the appearance of these formations on the skin are not fully understood. Nevertheless, scientists have proven that prolonged exposure to the sun and visiting a solarium promotes the growth of keratomas.
The most effective traditional medicine recipes
Drug and surgical treatment can be supported by traditional methods, which are less radical and absolutely safe.
We recommend reading: How to cure fungus between the fingers at home
Traditional medicine recipes cannot completely remove old plaques, but they can stop their spread and relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Walnut
The balm is prepared from walnut cores and sunflower oil in a ratio of 1:6. The oil is heated in a water bath and crushed fruits are added to it. Let it brew for 24 hours, then filter and apply to the affected areas several times a day. The course of treatment is two weeks.
Bay leaf
One teaspoon of bay leaf powder is ground with ten tablespoons of natural butter and a few drops of lavender oil are added. The resulting paste is applied to warts twice a day for three weeks.
Celandine
One part of the celandine herb ground into powder is mixed with five parts of melted pork fat. The resulting mixture is placed in the refrigerator until it hardens and used as an ointment for peeling and irritation. A few applications are enough to relieve discomfort.
Garlic
Grind the head of garlic on a fine grater until the juice appears. Then add a few tablespoons of heated natural honey and mix until it becomes a thick cream. Use three times a day.
Potato
One potato is crushed on a fine grater, then gauze is soaked in the mixture and the resulting compress is applied to the sore spot for an hour. You can repeat the procedure no more than twice a day.
Propolis
Recipe 1: apply a thick layer of propolis to large painful keratomas and cover tightly with a gauze bandage. Leave the compress on for five days, changing the bandage daily. Can be used once.
Recipe 2: a mixture of three onion peels and 200 ml of table vinegar is infused for two weeks. The resulting infusion is filtered and a tablespoon of propolis is added to it. The product is applied as a compress every day for a week, gradually increasing the procedure time from 30 minutes to two hours.
We recommend reading: Treatment of hidradenitis in women and men with folk remedies - recipes and prevention
Aloe
The cut aloe leaf is doused with boiling water, wrapped in a clean, thick cloth and placed in the refrigerator for two weeks. Cooled aloe leaves are cut into slices and applied as a compress.
In addition to external methods, infusions from agrimony root and celandine are also effective. A weak tea is prepared from dried plants and 100 ml is taken orally twice a day.
Taking baths with herbs rich in vitamin P will help soften keratinized plaques and relieve irritation.
Complications of keratoma
Most keratomas do not pose a threat to life and health. But the appearance of this formation cannot be ignored: you need to consult a dermatologist and follow his recommendations. If necessary, begin the prescribed therapy, or at an early stage of keratoma, treatment at home under the supervision of a specialist. This education does not happen on its own.
Once a defect is discovered, it must be observed and, if necessary, treated immediately. It has been established that in 8 - 35% of cases it degenerates into a malignant tumor - squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma. Many factors influence malignancy:
· irradiation - radioactive, ultraviolet;
· constant injury from clothing, straps, belts;
In addition to malignancy, as a result of mechanical damage to the keratoma, the penetration of papillomavirus or pathogenic microbes and the development of pyoderma (suppuration) or eczema can occur. The skin in this area will hurt and bleed for a long time. Treating the tumor at home in such cases will be ineffective.
But even an uncomplicated neoplasm causes aesthetic discomfort, even if it is located on closed areas of the body. Therefore, it is important to start treatment of keratoma in a timely manner at home or in an outpatient clinic under the supervision of a specialist.
Traditional treatment
The most effective method of treatment with kerasts is their complete removal using radical methods:
- Laser – within a few minutes, the affected tissue is burned once and for all. Wounds remain in place, in place of which healthy epidermis grows;
- Radiosurgery - tissue is excised using radio waves. A safe method that leaves no scars;
- Cryodestruction – a week after treatment with liquid nitrogen, the plaques completely disappear;
- Electrocoagulation – wound treatment occurs using electric current;
- Surgical removal - formations are removed with a scalpel. The method is traumatic, so it is rarely used.
Indications for removal of tumors may be the risk of their development into malignant tumors, inflammation, wounds, cosmetic discomfort or extensive lesions throughout the body.
Tinnitus: causes and treatment at home.
How to be beautiful at any age, read this article.
How to treat Helicobacter pylori, read this article.
How to treat keratomas (video)
Treatment of seborrheic keratoma with folk remedies, follicular and solar keratoma is a good attempt to fight the disease, but remember that only an integrated approach will give a high-quality result. Today you learned how to get rid of keratoma at home, which means that in just a few weeks your skin can become clean and healthy!!!
Keratoma
is a benign tumor that occurs on the outer part of the skin. At the beginning of the disease, it appears as a darker-colored spot on the skin, which subsequently begins to harden and peel off. The disease usually appears on exposed areas of the skin that are exposed to sunlight. Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, the outer skin scales grow and become keratinized. The growth of keratoma is often focal in nature, the tumor grows in size and similar formations appear in neighboring areas of the skin. The disease is not contagious and is not transmitted through contact with a healthy person. Typically, keratosis occurs in people over 35 years of age who are often exposed to the sun. Keratoma very rarely degenerates into a malignant formation, but self-diagnosis of keratosis is difficult. To accurately determine the type of tumor, you need to consult a specialist.
Possible complications
The only threat that keratomas pose is the development of skin cancer, which happens in 15% of cases when the disease is ignored.
If treatment is not started in time, large wounds can cause severe bleeding, open wounds and suppuration, which occurs due to microbes entering the tissues.
Compliance with preventive measures and treatment with traditional methods will help cope with the disease in the first stages of development, which will avoid surgical intervention and other radical methods.
What is a keratoma?
Keratosis is an age-related disease that affects people after 40-45 years. It is often called senile warts.
During the aging process, the human body ceases to produce and receive sufficient amounts of vitamins and microelements. Internal and external changes in the skin occur. Due to improper division of epidermal cells, dark brown spots begin to appear on the skin, which over time begin to thicken and become covered with hardened, flaky crusts. Senile keratoma can be single, or can be combined into groups. At the initial stage of the disease, the skin keratoma is small in size, but as the disease progresses, its size increases to 1-2 cm.
Causes
- metabolic disorders in the body lead to a lack of essential microelements and vitamins;
- hormonal imbalance and diseases of the endocrine system;
- long-term use of medications;
- negative effects on the skin of chemicals and solutions;
- constant friction of clothing elements of the same area of skin;
- long-term effects on unprotected skin from sunlight.