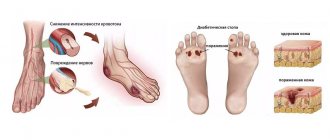
Trigeminal neuritis is sometimes mistakenly called trigeminal neuritis of the facial nerve, but more often another term is used - “neuralgia” - which literally means pain. This is an inflammatory process in the fifth pair of cranial nerves.
Our expert in this field:
Vasinkina Inna Yurievna
Neurologist
Call the doctor
Some facts about the disease:
- On average, it occurs in 6-8 people out of every 100,000.
- Women get sick more often than men.
- In most cases, the disease is diagnosed in people over 40-50 years of age.
There are two types of trigeminal neuralgia:
- Primary occurs as an independent disease.
- Secondary – a symptom of other pathologies.
How does the trigeminal nerve work?
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth pair of cranial nerves (there are 12 pairs in total - they innervate the organs of the head and neck). It is paired - that is, it is on the right and left. It consists of two types of nerve fibers - sensory and motor. After exiting the skull, the trigeminal nerve divides into three branches, which seem to cover the entire face:
- Ocular - is sensitive, innervates the eyeballs, eyelids, lacrimal sacs, mucous membrane of the nose and its paranasal sinuses, lacrimal gland, forehead skin.
- Maxillary - also sensitive, innervates the skin of the cheek, temple, teeth and gums of the upper jaw, mucous membrane of the palate, nose.
- Mandibular - responsible for both sensitivity and movement, innervates the muscles of mastication, muscles of the palate, eardrum, mucous membrane of the cheek, anterior 2/3 of the tongue, skin of the temple, the front of the ear and external auditory canal, teeth and gums of the lower jaw.
Symptoms of inflammation
The trigeminal nerve is the facial nerve with three branches. The first goes to the area above the eye, the second goes to the nose and the third goes to the lower jaw. A clear sign of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is pain that suddenly appears and is felt in all three branches at the same time or in only one. The syndrome comes on suddenly, lasts several minutes and gradually subsides. It is often preceded by itching of the facial skin and a feeling of pins and needles.
Read also: A temporary filling was placed after how long you can eat
In addition to acute pain, the pathology of the trigeminal nerve has other manifestations:
- headache, loss of strength, irritability;
- asymmetry in facial features;
- rash on the affected area;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- problems with the functioning of the ears and eyes;
- problems with jaw movement, pinched chewing muscles;
- tearfulness;
- deviations in the functioning of taste buds;
- numbness of areas of the face;
- voluntary contraction of facial muscles.
Additional Information. Painful “lumbago”, which causes inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, is provoked by the following factors: eating food of high or low temperature, touching the nose, gum or lip, a bright flash of light, a loud sound, turning the head, talking.
Most often, unilateral inflammation of the trigeminal nerve occurs. Although it happens that pathology affects both sides of the face at the same time.
Treatment of trigeminal neuritis
Typically, treatment of the disease begins with medications:
- Anticonvulsants . Usually the drug carbamazepine or phenytoin, oxcarbazepine is prescribed; the doctor selects the dose individually. Over time, these medications may become less effective, in which case your doctor will increase the dosage. However, anticonvulsants have some side effects that may make it difficult to use them.
- Antispasmodics . Used together with anticonvulsants. For example, a neurologist may prescribe baclofen for you.
- Physiotherapy . Diadynamic currents, ionogalvanization with novocaine, and ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone help to cope with the symptoms of trigeminal neuritis.
If neuralgia manifests itself in the form of severe toothaches, painkillers are used, and ointments with anesthetics are rubbed into the gums.
If medications no longer help, the neurologist raises the question of surgical treatment of trigeminal neuritis. The following operations are possible:
- Microsurgical decompression . During the intervention, compression of nerve fibers by blood vessels is eliminated. Typically the incision is made behind the ear. The operation effectively eliminates pain, but after it a relapse may occur, complications such as hearing loss, numbness of the face, paresis and paralysis of the facial muscles.
- Transection of nerve branches . In this case, the transmission of pain impulses is disrupted.
- Radiosurgery (gamma knife). A special device generates a high dose of ionizing radiation, which damages nerve fibers. If painful attacks begin to bother you again in the future, the procedure can be repeated.
There are other surgical methods for treating this type of neuritis.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
The trigeminal nerve provides sensation to the skin of almost the entire face and front of the head. It is mixed in structure, that is, it is responsible for both sensitivity and movement, but the motor fibers are thinner. Still, the trigeminal nerve is mostly sensitive. This determines the characteristics of the symptoms of the disease.
Traditional Treatments
Treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is very diverse and includes various types of therapy - from special massage to surgery.
Traditional treatment includes complex therapy, which is usually prescribed by the attending physician and includes the use of medications, physiotherapy, traditional medicine and, in the most severe cases, surgery.
For attacks of acute pain, medications are prescribed:
- analgesic effect (“Baralgin”, “Trimekain”);
- sedative effect (“Amitriptyline”);
- anti-inflammatory action (“Laferon”, “Gerpevir”);
- anticonvulsant action (“Oxcarbazepine”, “Clonazepam”, “Gabapentin”;
- vitamin complexes.
It is extremely important to understand that any drug treatment, whether tablets or injections, is prescribed by the attending physician. Any independent treatment can be deadly, because the dosage is strictly individual and can change several times during treatment.
The use of physiotherapy can reduce pain attacks, its main types used for this disease:
- ultraviolet irradiation of the face;
- laser therapy;
- electric currents;
- electrophoresis.
We recommend reading: Neurasthenia
As for surgical intervention, it is safe to say that today several methods are used in surgery to cure inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. The first of them is associated with eliminating the cause of the disease; for this purpose, craniotomy is performed and the vessel is restored to the correct position.
Of course, today, given the capabilities of modern medicine, this method is considered outdated and even controversial; the second method of treatment, associated with directing high-frequency current to the nerve, is now more often used. This method is called radiofrequency, and it is recognized as the best, since after using it, patients recover faster.
It should be said that surgical treatment is prescribed in cases where drug treatment has not brought any results.
You can also learn about the symptoms, treatment and prevention of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve from the following video:
What are the symptoms of trigeminal neuritis?
I am bothered by excruciating attacks of shooting, stabbing pains. They usually last for a few seconds or minutes and then suddenly go away. Most often, pain occurs in the area of innervation of the two lower branches of the trigeminal nerve: in the jaws, cheeks, teeth, gums, lips. In the area of innervation of the upper first branch of the nerve (forehead, eyes), pain occurs less frequently.
Usually only the right or left half of the face is affected. During an attack, a grimace of pain appears on the face, the person freezes, is afraid to move, and holds his breath. Sometimes the patient, on the contrary, begins to breathe heavily and frequently and rubs the sore spot.
Over time, attacks become more frequent and severe. There are certain “trigger zones” - most often they are on the lips and gums. Touching them, exposure to high or low temperature (cold or hot food) provoke painful attacks.
Often, pain due to neuritis is accompanied by vegetative symptoms, such as redness of the facial skin, lacrimation, and the release of large amounts of saliva.
Are you experiencing similar symptoms? Perhaps this is trigeminal neuritis or another disease, for example, arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint, multiple sclerosis. Only an experienced neurologist will be able to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve often occurs in middle-aged women. The development of symptoms begins with mild pain, which intensifies over time, beginning to cause great discomfort. The disease progresses rapidly and its course becomes paroxysmal.
- Brief pain. The main symptom of inflammation is a severe headache. Short, sharp attacks of pain lasting two to three minutes occur. Painful sensations periodically resemble short electric shocks.
- Prolonged pain. Constant pain can last for weeks, with relief occurring every few hours for a short time.
- Muscle spasms. Facial muscles contract suddenly and are accompanied by pain. Usually the spasm affects one half of the face.
- Muscle paralysis, jaw sagging, deterioration of lower jaw reflexes (Example: lack of jaw closure upon impact).
- Increased anxiety, insomnia.
Also, there is a loss of sensitivity, the area depends on which branch of the nerve is affected:
- Damage to the first branch (orbital nerve). The sensitivity of the eyelids, forehead, inner corner of the eyes, and upper part of the nose is impaired.
- Damage to the second branch (maxillary nerve). The upper parts of the cheeks, lips, teeth of the upper jaw, and the lower part of the nose lose sensitivity.
- Damage to the third branch (mandibular nerve). Disorders occur in the areas of the lower lip, chin, lower jaw, and cheeks. Paralysis of the masticatory muscles may occur.
Long term forecast
With treatment (and in rarer cases, without it), remission - the symptoms of trigeminal neuritis do not bother you for several months or even years. Many patients are helped by medications, but over time they begin to act weaker, and they have to resort to surgical treatments.
Frequent and severe pain attacks can reduce performance and quality of life. In young patients, the prognosis is more favorable, in older people (and it is in them that the disease occurs more often) it is more serious.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
The cause of trigeminal neuritis is not always found. In this case, the disease is called idiopathic . If the damage to the nerve trunks is caused by some other disease, they speak of symptomatic , or secondary , neuritis.
Most often, the disease develops as a result of compression of the nerve by improperly located vessels. In most cases, the superior cerebellar artery is to blame.
Modern medicine sees the mechanism for the development of inflammation and pain as follows. Chronic compression causes the trigeminal nerve to lose myelin , a sheath that is made of fat and is important in conducting nerve impulses. An inflammatory process develops. Subsequently, degeneration of axons - the long processes of nerve cells that make up the nerve fiber.
Symptoms of pathology
Quite often people do not know exactly how neuralgia manifests itself. That is why they do not know what they are dealing with, and therefore cannot begin treatment on time. It will be useful to familiarize yourself with the main symptoms in order to recognize them in time and take measures to improve your well-being. Signs can manifest themselves in varying degrees, so it is difficult to say for sure how intense they will be in a person.
Symptoms:
- Pain syndrome. It necessarily occurs with inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. It can be localized at one point, directly from the edge of the mouth or nose to the gums or teeth. Quite often the disease affects only one side of the face, mainly the right.
- The sensation of pain is paroxysmal, and it has a burning and shooting character. The attack occurs several times a day and once every fifteen minutes. Moreover, it lasts from 30 to 120 seconds, it all depends on the individual characteristics of the patient.
- As soon as a sharp pain occurs, a person may freeze with a grimace on his face. This doesn’t last long, but it becomes noticeable to the people around you.
- Quite often, the problem area of the face can become hot.
- Patients experience increased salivation and lacrimation. A runny nose may also occur due to illness.
- Direct irritation of the receptors leads to the fact that the facial muscles begin to twitch. Muscle spasms in the facial area are possible.
Although the manifestations of the disease are noticeable externally, visual examination alone is not enough to make a diagnosis. You will definitely need to analyze the symptoms that worry the person. A specialist can also refer a person for certain examinations, based on the results of which it will be possible to draw an unambiguous conclusion about the state of health.
What other causes can lead to trigeminal neuritis?
In addition to vascular compression, other causes can lead to the disease:
- Age-related changes in the body.
- Compression of the nerve branches in the bone canals of the skull in which they pass. These canals can be narrowed from birth, or as a result of certain diseases: caries, sinusitis.
- Compression by intracranial tumors.
- Injuries to the face, head.
- Multiple sclerosis. This is a chronic disease in which the myelin sheath is destroyed. Trigeminal neuritis affects 3-4% of patients with multiple sclerosis.
- Postherpetic neuralgia. Its cause is herpes zoster.
Causes of nerve inflammation
The main reasons contributing to the development of inflammation are considered to be:
- Hypothermia of the face,
- Head injury,
- Nerve compression due to vascular diseases and tumors,
- Multiple sclerosis,
- Oral diseases, etc.
Inflammation can be primary, for example, as a result of hypothermia, and secondary, i.e. be a consequence of ENT diseases and brain diseases.
Causes of pain attacks in trigeminal neuritis. What are triggers?
Triggers are irritants, “triggers” that provoke an attack of pain. These can be a variety of mechanical or temperature effects on the skin of the face and mucous membranes.
Most often, the following factors act as triggers: shaving, eating food (especially cold or hot), any touching the face, drinking, talking, brushing teeth, wind, applying makeup, washing, smiling. When habitual daily actions always lead to excruciating pain, this significantly reduces the quality of life and interferes with work.
When you see your doctor, tell your doctor what triggers lead to attacks in your case.
Herbal infusions for the treatment of trigeminal nerve diseases
The following infusion is prepared from mint, valerian and St. John's wort: 200-250 grams of fresh mint are mixed with one hundred grams of valerian and St. John's wort. Next, the herbs are poured with water at the rate of a couple of tablespoons of herbs per 0.5 liters of water, brought to a boil and boiled for 15 minutes. After boiling, the infusion should be strained and left for five hours in a place protected from the sun. To treat various neuralgia, this infusion should be taken three times a day, a tablespoon.
Chamomile and burdock are also good for coping with neuralgia. These herbs can be used for infusion and in dried form. Fill 150-200 grams of herbs with water (about 0.5 l), bring to a boil and boil for 15-20 minutes. The prepared infusion should be carefully strained and infused for at least one day. It is advisable to drink this infusion a couple of hours after eating.
Aloe is one of the most popular medicinal plants that can be grown on your own windowsill. Aloe is used to treat many diseases, including inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. For treatment, the juice of a plant that is no more than 3 years old is best suited. Squeeze juice from freshly picked aloe leaves and take 1 teaspoon orally. Drink aloe juice at least three times a day before eating.
Birch sap is also quite a good helper in the fight against many diseases, including neurological ones. The composition of birch sap can be called unique; the content of useful substances in it can not only give vitality to the body, but also treat many diseases. To treat diseases of the trigeminal nerve, birch sap is used not only for oral administration, but also for washing the face. It is recommended to drink birch sap at least 5 glasses a day, and you should wash your face with the sap at least a couple of times.
How does the treatment of neuritis depend on the causes?
If the cause of trigeminal neuritis is not known, all that remains is to deal with its main manifestation – pain. The neurologist prescribes various medications, and if they stop helping, he recommends surgery.
If the cause of the disease is known, you need to try to eliminate it. For example, if a patient is diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, special therapy is prescribed that helps slow down the progression of the pathology. If the nerve is compressed by an artery or the walls of a bone canal, the compression must be removed.
Get a consultation with a doctor
Sometimes, before the correct diagnosis is finally established, a patient suffering from trigeminal neuritis has to see more than one doctor. It is extremely important to start treating the disease as early as possible. It has been proven that the longer a person suffers from trigeminal neuralgia, the more difficult it is to cope with the pathology.
Causes
There are many reasons that lead to the development of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. It is definitely quite difficult to determine which factor led to the onset of the disease.
For this reason, it is recommended that a person consult a doctor so that he can find out the cause of the disease, as well as find out an approximate treatment regimen. If possible, provoking factors should be avoided to reduce the likelihood of developing the disease.
Causes:
- Neoplasms, as well as adhesions that affect the branches of the nerve. They quite often lead to the development of inflammation, and it is extremely important to accurately determine whether they are dangerous to the body.
- Dental problems. Often, pulpitis, periodontitis, and even a poorly installed filling on a tooth can cause problems with the trigeminal nerve.
- Trauma to the face and jaw. In such a situation, a person may experience pain due to damage to nerve fibers.
- Vascular atherosclerosis. It causes cholesterol plaques to appear, which significantly impair blood flow. Because of this, the nutrition of blood vessels becomes worse, so it will be extremely important to fight atherosclerosis.
- Infections. In particular, inflammation is often caused by bacteria that live in the oral cavity. In such a situation, you should not be surprised that the nerve fibers become inflamed.
- Hypothermia. If the patient has been in a draft for a long time, then he may experience problems with the trigeminal nerve. In such a situation, we can recommend that you be more attentive to your health in the future in order to avoid the occurrence of pathologies.
It should be noted that in some situations the disease is provoked by existing problems with the body. These may include multiple sclerosis, herpes infection, vascular problems and psychogenic diseases.
Even metabolic disorders can lead to a person’s nerve becoming inflamed. For this reason, it is recommended to undergo a professional diagnosis to ensure that there are no other health problems. You shouldn’t neglect existing pathologies if you don’t want to suffer from their complications later.
Diagnosis of trigeminal neuritis: what happens during an appointment with a neurologist?
An appointment with a doctor begins with a conversation. First of all, it is important for a neurologist to get answers to three questions:
What is the nature of the pain? Is it typical for this disease ? With trigeminal neuritis, pain attacks occur suddenly, they are strong, painful and pass quickly.
Where does the pain occur ? When the trigeminal nerve is damaged, pain is localized on the face, in certain places.
What triggers lead to seizures ? Usually this is touching the face, exposure to wind, high and low temperatures.
You will be asked how long you have been experiencing symptoms, whether you suffer from any chronic diseases, and whether you are receiving any treatment. Then the neurologist will examine you and press on certain points on your face where the branches of the trigeminal nerve enter the skin. A general neurological examination will be performed to diagnose any possible medical conditions that may be causing your symptoms.
Effective folk remedies for the treatment of the trigeminal nerve
Trigeminal neuralgia refers to a painful disorder of one or more branches of the facial nerve. Sensations from the face are transmitted to the brain using this nerve. People with this condition experience pain in the face, and some experience pain closer to the ears.
Patients complain of debilitating pain that can last for a long time. As a rule, trigeminal neuralgia is caused by compression of blood vessels that are located close to each other, and the reason may also lie in the loss of the protective covering.
What diagnostic methods can a doctor prescribe for trigeminal neuritis?
The disease can be caused by various reasons, sometimes very serious (for example, cancer). Diagnosing them is not always easy. Depending on your complaints and information obtained during the examination, the neurologist may prescribe various instrumental studies and laboratory tests.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the head is most often used. This diagnostic method helps to identify pathological changes in the brain characteristic of multiple sclerosis and intracranial tumors.
Medical doctors adhere to modern current standards - this guarantees that you will be prescribed all the tests necessary in your case, the doctor will not miss anything. At the same time, the coordinating doctor in our clinic will make sure that only truly necessary procedures are prescribed to you, so that you do not overpay for unnecessary things. All types of diagnostics are carried out using our medical center’s own equipment.
The material was prepared by Natalya Yurievna, a neurologist at the Medicine 24/7 clinic, Candidate of Medical Sciences Lasch.