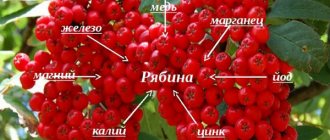
Chemical composition
All parts of the wolfberry contain toxic substances: coumarins (dafnetin, dafnin, etc.), diterpenoids (meserein, dafnetoxin).
Mesereine affects the skin, causing blistering and redness, and the mucous membranes, causing upset and burning of the stomach. In addition, it exhibits mutagenic properties. Daphnine belongs to the group of antivitamins K and can cause increased bleeding.
Wolf bast flowers contain fatty oils that actively affect the skin, sitosterol, benzoic acid, coumarins and flavonoids. Resins, dyes and wax were found in the bark of the wolfberry. The berries of the plant are a source of essential oil, bitter and coloring substances, fat and coccognin.
Signs of poisoning
Having understood what a wolf's bast is and what it looks like, you can begin to describe the symptoms of poisoning.
Often, either small curious children or careless adults who have no experience of living in rural areas suffer from the poison of its fruits. The desire to eat unusual berries can even lead to death if appropriate detoxification measures are not taken in time. Remember that even 6-7 berries can become a lethal dose.
The manifestation of poisoning begins with:
- burning or scratching sensations in the mouth, larynx (similar to the sensation of a sore throat);
- stomach pain;
- excessive salivation;
- vomiting;
- constant feeling of thirst;
- diarrhea.
A little later, the second phase of symptoms begins:
- vertigo (dizzy),
- lethargy,
- bloody discharge,
- convulsions.
All this leads to heart failure, which causes a tragic outcome.
A wolf's bast is dangerous even when an open area of skin comes into contact with the bark. People with hypersensitive skin may develop ulcers even after a single touch.
If a person finds himself in a place with a large concentration of bushes, then the vapors of its sap from the bark can irritate the respiratory system, causing others to sneeze, cough and suffer from a runny nose. And if you stand near a flowering plant for a long time, it will give you a dull headache.
Indications for use
Indications for the use of wolf bast in folk medicine are:
- Severe rheumatic and neuralgic pain;
- Gout;
- Radiculitis;
- Paralysis;
- Scrofula;
- Various boils;
- Tumors of the esophagus, throat and uterus;
- Thrombophlebitis.
If you have poor appetite and fatigue, it is recommended to eat one dried wolf bast fruit once a day. Sometimes plant preparations are prescribed for jaundice, tuberculosis, dysentery and colds.
In homeopathy, wolfberry is used for irritation and suppuration of the skin with the formation of pustules and blisters, cracks in the skin, ulcerative rashes with pale yellow crusts, convulsive pain in the bladder, and to treat enlarged testicles. Homeopathic preparations of wolf's bast are called Mezereum.
Description of the wolf's bast bush
A perennial, deciduous, low-branched shrub, wolf's bast, is known primarily for the poisonous effect of its berries. It is quite common in the wild, which makes it highly likely to be confused with other berries.
Wolf's bast bushes grow low. Their height does not exceed 1 m. With deliberate cultivation of the plant, the height of the shoots can increase to 2.5 m. In nature, conditions suitable for this are extremely rare.
In spring, bast begins to bloom before greenery appears on the shoots. The flowers are located in the axils left after the leaves fall before wintering. The flowers are collected in small inflorescences of 3 pieces. The flowers are fragrant. The shrub is a spring honey plant.
A rare shrub in which flowering occurs before landscaping. Flowers can be recognized by the following characteristic features:
- Pink color. Rarely, you can also find white flowers;
- Pleasant scent reminiscent of hyacinth;
- Externally similar to lilac.
They can be observed from mid to late spring. Then the fruits appear, which become red during ripening. The shape of the berries is ovoid, like the leaves. The bark on the entire surface of the plant is gray-brown. A peculiarity of the shrub is that the old shoots have a yellowish-gray bark that is very wrinkled. And young shoots are somewhat pubescent. This feature helps to recognize a wolf's bast when found in coniferous and mixed forests.
Contraindications
The wolfberry should be used carefully, following the indicated dosages. Taking 10 berries of the plant can be fatal.
During the use of wolf bast, it is necessary to monitor the patient’s well-being. At the first signs of wolfberry poisoning (vomiting, diarrhea, salivation, bloody urine, abdominal pain), the drug should be discontinued and immediately seek medical help.
Plant-based medicines are strictly contraindicated for children and pregnant women.
Use in folk medicine
How can a poisonous plant be useful for the human body? The dangerous composition discourages applications in medicine and cosmetology, but in small doses the poisons do not harm the body.
Before making folk remedies from wolfberry, consult your doctor.
Among the useful properties:
- Helps relieve epileptic seizures.
- Relieves pain syndrome.
- Has a laxative effect.
- Helps fight insomnia.
- Used for sore throat and other blister conditions.
Thanks to a natural sleeping pill, a person will fall asleep faster. A laxative will help overcome the problem of constipation.
For recipes for preparing folk remedies at home, see the table:
| Recipe | Required ingredients and description |
| Toothache powder | Both flowers and leaves are suitable for this recipe. Take the ingredients in equal parts and dry them for several days in the sun or on a windowsill. Prepare a powder from the dried mixture. Apply the mixture, slightly moistened with water, to the sore spot. After 10-15 minutes, when the product has taken effect, rinse your mouth with water. |
| Sore throat decoction | Pick a few flowers from the plant. Prepare medicinal tea for purulent diseases of the oral cavity: brew the petals with boiling water and leave to steep for half an hour. When the tincture has cooled a little, gargle. You can also take the decoction orally, 5 drops 3 times a day. |
| Berry tincture with alcohol | This remedy is used externally to cope with pain from rheumatism or other back pain. Collect honeysuckle berries, you can add a little bark. The tincture does not require many dangerous ingredients. For 1 liter of vodka or alcohol, take 8-9 berries and the same amount of bark. Leave the alcohol composition in a dark place for a week. After 7 days, you can lubricate the inflammatory areas where the pain is concentrated |
| Natural sleeping pill | For the recipe it is better to take the roots. For 200 ml of water, take only a couple of grams of grated product. The broth should infuse for about half an hour. After preparation, you need to take half a glass of sleeping pills and after 30 minutes you will already want to sleep |
Important! People prone to allergic reactions should not use traditional methods. Should not be used by pregnant and lactating children, as well as children under 18 years of age.
Home remedies from wolf bast
- Decoction. Pour 2 g of plant flowers into 20 ml of boiling water, put on fire and boil for 20 minutes. Then remove the broth from the heat and immediately strain, squeezing out the raw materials. Bring the resulting volume to 250 ml. Take 5 drops three times a day;
- Powder. Collect the flowers of the plant and grind into powder. Use for toothache, rubbing into the sore spot. After the procedure, you must rinse your mouth with boiled warm water;
- A decoction is a sleeping pill. Pour 4 g of wolf bast roots with a glass of boiling water, place in a water bath for 30 minutes, then leave for 15 minutes and strain. Take one teaspoon before meals twice a day;
- Fruit tincture. Pour 1 g of plant fruits into 0.5 cups of 70% alcohol and leave for infusion for a week. Then strain the finished product. Take three times a day before meals in diluted form (add two drops of tincture to 1 tablespoon of water).
What does a wolf's bast look like in pictures?
The shrub is small in size and can reach a height of 1 meter. In artificially created favorable conditions, specimens can grow up to 3 meters.
Depending on the time of year, the wolfberry forest looks different:
- Spring. The bush resembles the Chinese sakura tree in appearance. Fragrant pink flowers bloom on the branches; there are practically no leaves on the stems.
- Summer. After flowering, red oval fruits appear from tricolors, reminiscent of rose hips or rowan berries. The red balls are grouped very closely. There are more leaves, but they have a gray tint.
Important! It is difficult to confuse a wolfberry bush with another plant. The leaves and berries are long, egg-shaped.
Description of the plant Wolf's bast (Common wolfberry)
Description of Wolf's Bast (Common wolfberry).
- Literary names of the plant: Common wolfberry, Deadly wolfberry;
- Latin (botanical) name of the plant: Daphne mezereum;
- Generic name of the plant: Daphne;
- Common names of the plant: Wolf's bast, Wolf's berry, Wolf's berries, Plokhovets, Pukhlyanka.
These are just the most common names among the Russian-speaking population. Almost all of these names came to us from the history, myths and legends of Wolf's Bast
.
Due to its beneficial healing properties, Wolf's Bast (Wolf's Bast)
used in both official and folk medicine.
Wolf's bast (Wolf's bast) is
also for decorative purposes.
In various photos of the Wolf's bast (Wolf's bast)
you can see the main structural features and appreciate its beauty.
Wolf's bast or wolfberry is a poisonous plant listed in the Red Book, which is also called wolfberry, boletus pepper, boletus, or daphne. The second name is Latin, used by botanists and given to the plant in honor of the nymph Daphne, who turned into a laurel tree, avoiding the love of the god Apollo.
This is a deciduous shrub, the height of which depends on the growing conditions and can range from 40 cm on slopes to 2.5 meters in cultivated plantings. Shoots have yellowish-gray bark, young branches are pubescent with tight-fitting villi. The leaves are collected at the ends of the branches, obovate-lanceolate. The flowers are bisexual, sessile, bloom in spring in April-May before the leaves appear, fragrant. The fruits are red drupes. Prefers dark coniferous forests, grows along river banks, on forest edges, rarely forms thickets.
Despite the fact that the entire plant is poisonous, it has long been used in folk medicine and homeopathy. Used internally as a decoction of the bark, a few drops. It can also be used as a tincture of twigs with flowers in alcohol or vodka for neuralgic and rheumatic pain. The collection is carried out with gloves, avoiding contact of the plant juice with the skin and mucous membranes. If signs of poisoning appear, it is necessary to take the victim to a doctor as quickly as possible.
Wolf's bast (Vulcheyagodnik vulgaris) is listed in the red books.
The medicinal plant was included in its Red Book
: - Altai Republic; - Altai region; - The Republic of Buryatia; - The Republic of Moldova; - Republic of Tatarstan; - The Republic of Moldova; — Bryansk region, Vladimir region, Irkutsk region, Irkutsk region, Kaluga region, Kurgan region, Kursk region, Lipetsk region, Moscow, Murmansk region, Omsk region, Oryol region, Penza region, Ryazan region, Samara region, Saratov region, Tula region , Tyumen region; - Latvian republic; - Republic of Lithuania; — Ukraine: Donetsk region, Zhytomyr region, Ternopil region; - Chuvash Republic.
Additional information about the plant Wolf's Bast (Common wolfberry)
Medicinal plants ozonit.ru Encyclopedia of medicinal plants Information about the plant Wolf's bast (Wolf's bast) History, myths, legends about the plant Wolf's bast (Wolf's bast) Description of the plant Wolf's bast Wolf's bast (Wolf's bast) Collection, drying and storage of the plant Wolf's bast Wolf's bast (Wolf's bast) Properties of the plant Wolf's bast Wolf's bast (Wolf's bast) Composition of the plant Wolf's bast Wolf's bast (Wolf's bast) Application of the plant Wolf's bast Wolf's bast (Wolf's bast) Contraindications of the plant Wolf's bast Wolf's bast (Wolf's bast) common yearling) Growing the plant Wolf's bast Photo of the plant Wolf's bast Wolf's bast (Common wolfberry)
| Share this article with your friends! |
Treatment with wolf bast
This medicinal plant is used for many diseases and symptoms:
- painful bone pain at night
- damage to bones and periosteum
- herpetic rash and many other skin diseases (rash, itching, lichen)
- pain in the teeth, especially at night
- gastrointestinal diseases
- itching and discharge from the genitals
- gland tumor
- chronic rhinitis
- neuralgic pain
Previously, wolf bast was used as a laxative. However, at the moment it is not recommended to use it internally due to its toxic substances.
Also, it should be used externally only in homeopathic dosages prescribed by a doctor. When applied to the skin, wolfsbane can cause harm to the skin with unnecessary abscess and irritation.
Drugs that have antiepileptic, antibacterial, antitumor and analgesic effects are made from wolf bast. By the way, quite often this plant is used in the fight against cancer.
Along with the fruits, wolf bark is also used in medicine. The medicinal properties of the bark are effective in treating cancer of the uterus, esophagus, larynx and mouth. Ripe berries have a healing effect in cases of sarcoma.
For treatment, infusions and decoctions of the bark and dried berries of wolf bast are used. These medications are taken in a few drops per day. Wolfweed bark is available in the form of crushed powder, infusion or pills.
Preparations from wolf bast are also prescribed for the treatment of cough, tuberculosis, and fever. In moderate homeopathic doses, wolfberry is used to treat diseases of the stomach and intestines. In addition, it has a tonic effect, eliminates chronic fatigue, and improves appetite.
During treatment with this plant, poisoning, side effects or an overdose may occur. It is enough for a person to consume just a few berries and something irreparable can happen.
Poisoning can be identified by several symptoms: increased salivation, blood in the urine, abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea. Therefore, it is important to take immediate measures: rinse the stomach, pour in Vaseline oil; To eliminate irritation in the stomach, you need to take anesthesin, the mucous membranes should be lubricated with dicaine.
It must be remembered that wolf bast is a very poisonous plant, although it has beneficial properties that are used in the treatment of many diseases. It is important to follow your doctor's instructions and strictly take medications as directed.
Preparation and storage of wolf bast
All parts of the wolfberry are used for medicinal purposes. The bark should be harvested in early spring. It must be dried outdoors (in the shade) or in a well-ventilated area. In this case, the raw materials are laid out with the inside out (it is necessary to ensure that the strips of bark do not stick together). As for the fruits, they are harvested in June-July. It is better to dry fruits in a special dryer or oven at low temperature.
Due to the fact that wolfberry is a poisonous plant, you need to work with it wearing gloves and taking precautions.
Use in everyday life
Wolfberry berries can be used to expel worms from dogs and cats. Their tincture is an effective remedy in the fight against insects. In turn, the bark is used as a dye for wool.
The main medicinal raw material for wolfberry is usually the bark of the plant. It must be collected before the bush begins to flower, that is, in early spring or in the first half of summer. To do this, it must be cut from the trunk and thick branches into thin strips and laid out in one layer (inside up) in a dry and regularly ventilated room, leaving there until completely dry.
Until the bark dries, that is, it is in a wet state, you can touch it only with gloves, since getting the juice on the skin will easily provoke the formation of abscesses and ulcers, and with prolonged contact it will lead to general poisoning of the body.
They begin collecting the fruits of the bush at the end of summer, after which they need special drying at low temperatures. Sometimes even branches with leaves are used to prepare the compositions, which are also carefully cut from the bush and, collected in small bunches, hung in the attic or in another dark and ventilated place.
Do not forget that even after drying out, the plant does not lose its toxic properties, so the harvesting process should not be entrusted to children, and the finished raw materials should be stored away from them, in labeled containers. When processing a plant, it would also be useful to use a respirator to protect you from inhaling the toxic substances it emits.
Wolf's bast: pharmacological properties and application
The bark and fruits of the plant contain the oxycoumarin umbelliferone, the glycoside daphnin, organic acids, dafnetin, coloring, bitter, tannins, fatty and essential oils, triterpene saponins, and flavonoids. The berries also accumulate coccognin, a poison that causes severe poisoning (marsh wild rosemary and celandine)
The plant is used mainly for external treatment as a highly irritating agent. When used internally, drugs made from wolfberry have a hypnotic, antiepileptic, laxative, antibacterial, analgesic, and antitumor effect.
Folk recipes
Since ancient times, an alcohol tincture of wolf bast fruits has been used externally for paralysis, gout, rheumatism, neuralgia, tumors and abscesses, rubbing it into diseased areas of the body. The crushed bark of the bush was applied to areas affected by the bites of rabid dogs and snakes. To prepare, dry fruits (1 g) are poured with alcohol (100 ml), left for two weeks. (burnet - use and treatment)
A decoction of the roots is effective against inflammation of the colon, seizures, insomnia, dysentery, jaundice, as well as diseases caused by single-celled organisms. To prepare, pour boiling water (100 ml) over the roots (2 g), keep on low heat for half an hour, strain, squeeze. Take 5 drops after meals three times a day for five days.
Tincture of branches and bark can be used externally for conjunctivitis, diathesis, furunculosis, skin tuberculosis, rheumatism, neuralgia, paralysis. It should be taken internally for dropsy of the abdomen, cough, sore throat, high temperature, fever, cancer and as a laxative. In rare cases, it is used as an anthelmintic. To prepare, you need to pour the bark (1 g) with alcohol (100 ml), leave for a week, shaking occasionally. Take 2 drops three times a day before meals. (St. John's wort has medicinal properties)
Coumarin, which is contained in wolfberry fruits, reduces blood clotting in thrombophlebitis. For blockage of blood vessels, itchy dermatosis, and toothache, drugs are prescribed externally and internally. For fatigue, atherosclerosis, paralysis and poor appetite, it is recommended to take one wolfberry per day orally.
Wolf bast can be used to prepare an ointment for the treatment of neuralgia. It is necessary to mix the fruit tincture (20 ml) with lanolin (50 g), gradually adding Vaseline (50 g). Affected areas should be lubricated at night. The powder made from the bark should be sprinkled on ulcerated scrofula, and the powder from the leaves should be sprinkled on cancerous ulcers. (care for the skin around the eyes)
Contraindications
Wolfberry compositions must be used with caution. When used externally, they can cause irritation and burns of the skin, and when used internally, they can cause fever, vomiting, convulsions, stomach ulceration, loss of strength, intestinal upset, loss of consciousness and increased bleeding. Ten to fifteen fruits are a lethal dose for the human body.
“A wolf in sheep’s clothing” - this is how one can characterize this incredibly beautiful when flowering, but treacherous plant. It can easily kill a person, but it is expected to help treat cancer. This article tells how to recognize wolf's bast among other shrubs, why it is called that, how and where it can be used, and what to do if it is poisoned by its scarlet berries.
Wolf's bast - appearance of berries
Healing decoctions
In each specific case it may be different. It is necessary to take into account the state of the body. Sometimes herbs contain toxic substances that can put additional stress on the liver. Therefore, making a decision on your own would be too rash a step. One of the most popular healing decoctions is the following:
- Chaga extract – 200 g.
- Rose hips, pine cones and yarrow grass - 50 g each.
- Wormwood - 5 g.
All ingredients need to be crushed, mixed and poured with three liters of hot water. The container is wrapped and left for three hours. Then put the pan on low heat for 1.5 hours. She should only languish a little.
The finished broth is wrapped again and left for a day. Now the drink should be filtered, add 250 g of cognac and 500 g of honey, 200 g of aloe juice. It should be stored in glass containers at room temperature. Take a teaspoon 5 times a day. Judging by the reviews, cancer treatment with folk remedies is effective in the initial stages. If the disease is already very advanced, then only chemotherapy and surgery will help. But you should remember, like pharmaceutical drugs, it is not recommended to abuse decoctions.
What is the danger of a wolf's bast?
Since the plant grows in almost all Russian forests, every person should know about the poisonousness of wolf bast. The whole plant, especially its bark, is dangerous to health, although most often a person suffers from eating wolfberry berries. The juice of the plant contains substances that negatively affect the condition of the human body. They can cause:
- redness of the skin;
- bleeding;
- burning sensation in the mouth;
- nausea and vomiting;
- swelling of the skin, blisters and ulcers.
Children should treat the plant with extreme caution, as symptoms of poisoning can cause convulsions, which can lead to death.
Use in medicine
Despite its poisonous qualities, proper use of the plant can only bring benefits to the human body. For medicinal purposes, the root and berries of wolf bast are used. In order not to harm the body, we advise you to harvest wolfberry only to those people who know all the intricacies of preparing the plant for medical use.
Wolf's bast has antibacterial, laxative, hypnotic and antitumor effects, so it is often used in the treatment of:
- insomnia;
- dropsy;
- rheumatic diseases and gout;
- stomach cancer;
- dysentery;
- toothaches.
Treatment with wolf bast should be approached with great caution.
Medical assistance to the victim
In case of poisoning by Wolfberry, medical attention is required. Using self-medication methods is extremely dangerous; it can only worsen the victim’s condition. You cannot hesitate; providing first aid and quickly transporting a poisoned person to a hospital will save a person’s life. How is the treatment carried out?
The main cause of poisoning is the penetration of toxic substances into the gastrointestinal tract, which contributes to irritation of all mucous membranes of the body. Consequently, any good doctor will first begin to work to remove these substances from the patient’s body as quickly and efficiently as possible:
- gastric lavage,
- introduction of Vaseline oil,
- introducing pieces of ice inside,
- treatment of mucous membranes with dicaip.
Skin covered with blisters or burns is treated mainly with Vishnevsky ointment. Levomycetin and streptocide are also used for treatment.
Toxic substances have a huge impact on the cardiovascular system of the body. It is from heart failure that those who try these wolf berries die, so the poisoned person is prescribed strophanthin and other drugs that will restore the functioning of the heart.
It is important to remember that in case of Wolf Bast poisoning, laxatives should not be used, since the intestines are already in a mode of rapid cleansing of the body.