Laryngitis is an inflammatory process of the larynx, which is characterized by a violation of its functions. Almost every person has suffered from laryngitis at least once in their life, and some cannot get rid of the obsessive symptoms of the disease for years.
They cause a lot of inconvenience, distracting from work and everyday worries. And people whose profession involves straining their vocal cords (announcers, actors, singers) may even be at risk of losing their voice. It is necessary to treat laryngitis in adults to avoid complications.
Forms of the disease
There are two forms of the disease: acute and chronic. Their main difference is the duration of the disease over time.
Determining the form is necessary for further effective treatment of the patient.
Acute laryngitis
Laryngitis is considered acute if it lasts up to 3 weeks of illness. It is usually caused by bacterial or viral etiology, overstrain of the vocal cords and irritants (cigarette smoke, chemicals). Almost always, acute laryngitis begins suddenly and occurs against a background of high body temperature and severe sore throat.
There are 3 types of acute laryngitis:
- subglottic;
- catarrhal;
- infiltrative.
This distribution occurs according to the localization of the pathological process, depending on which the clinical picture of the disease and its further treatment will differ.
Chronic laryngitis
If laryngitis lasts more than 3 weeks, then it is called chronic. The chronic form of the disease can be a continuation of the acute form. Often its exacerbation is provoked by gastroesophageal reflux, smoking, and allergies. Chronic laryngitis is not always accompanied by elevated body temperature, and sore throat is less pronounced than in the acute form of the disease.
The disease is aggravated by accompanying factors:
- decreased immunity;
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- inhalation of irritating gases and dangerous vapors;
- diseases with severe cough (bronchitis, pneumonia).
Classification and signs of laryngitis
Laryngitis can manifest itself in different ways. Its symptoms depend not only on the form, but also on the affected area of the larynx.
Allergic form
The allergic form of laryngitis occurs more often in children, but it is not uncommon in adults. It often continues from childhood, acquiring a chronic form, and sometimes it appears for the first time in adulthood.
The cause of this form is the contact of the allergen with the mucous membrane of the larynx. This occurs after respiratory viral diseases or inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
The mucous membrane becomes more sensitive to the effects of pathological factors. After contact with the allergen, swelling of the larynx is observed, covering some of its areas or completely. Swelling leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the larynx and makes breathing difficult.
How to treat laryngitis in adults depends on the form. If it is allergic laryngitis, you need to take an antihistamine
Symptoms of allergic laryngitis:
- hoarseness of voice or complete loss of voice;
- "barking" cough;
- difficulty breathing with prolonged inhalation;
- dyspnea;
- cardiopalmus;
- noisy breathing with retraction of the supraclavicular fossa;
- pale skin, sometimes with cold, sticky sweat.
Atrophic form
The atrophic form of laryngitis is characterized by thinning of the laryngeal mucosa and sclerosis of regional capillaries. This form of laryngitis occurs in most cases in adults; it occurs extremely rarely in children. Among all forms, it accounts for 10% of cases of the disease.
The main causes of the atrophic form of laryngitis are the following factors:
- frequent diseases of the respiratory system – contribute to a decrease in the body’s protective functions;
- hormonal imbalance - hormonal imbalance of the thyroid and pancreas can provoke changes in the structure of the mucous membrane of the larynx and vocal cords;
- professional factor - constant presence in poorly ventilated areas, with high concentrations of chemicals, low or high temperatures, or professions with constant tension on the vocal cords (speakers, singers, actors, teachers);
Symptoms of the disease:
- hoarseness of voice;
- dry throat;
- obsessive dry cough;
- "lump in the throat.
Hemorrhagic form
Hemorrhagic laryngitis is most often provoked by a viral disease and is characterized by hemorrhages under the mucous membrane of the pharynx and larynx. The reason for this is the ability of the virus to infect the wall of blood vessels, damaging it and causing bleeding.
Causes of hemorrhagic laryngitis:
- influenza or other acute respiratory viral infection;
- prolonged debilitating cough;
- prolonged singing without interruption.
Symptoms of the disease include a cough without producing sputum and a feeling of a foreign object in the throat. A characteristic sign of the hemorrhagic form is sputum streaked with blood.
Morphologically, dilated vessels and areas of hemorrhage are found on the mucous membrane.
Hypertrophic or hyperplastic form
Hypertrophic laryngitis is characterized by proliferation of the epithelial layer and can lead to closure of the glottis. Typically this form of the disease occurs in older people.
The most common causes of the disease are the following factors:
- treatment in late stages of the disease;
- insufficiently treated laryngitis;
- development of complications after infectious diseases;
- the presence of chronic infectious diseases;
- decreased immune function of the body;
- age-related atrophy of the laryngopharynx muscles;
- dystrophic disorders.
Symptoms of this form consist of the following complaints:
- severe pain when coughing and swallowing;
- "barking" cough;
- the presence of thick mucous content in the larynx, which is difficult to cough up;
- shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
There are 2 types of hypertrophic laryngitis:
- local – damage to a small area of the larynx;
- diffuse - covers most of the larynx (it may hide laryngeal cancer).
Fungal form
Candidiasis laryngitis is a form of the disease that is provoked by a fungus. It occurs in people with reduced immunity. In this case, the mucous membrane becomes favorable for the proliferation of fungal microflora here, which contributes to the development of the disease.
Main symptoms:
- white plaque on the back wall of the pharynx, larynx, sometimes they are present on the tongue and the inside of the cheeks;
- inflammation and swelling of the larynx;
- difficulty swallowing food and saliva;
- a sore throat;
- signs of general intoxication.
The plaque has a special appearance: it is loose, similar to a curd mass, easily removed with a gauze cloth, quickly forms and spreads to other walls.
Diphtheria form
The diphtheria form of laryngitis is very dangerous, since it produces diphtheria films, the aspiration of which can threaten the patient’s life. It occurs more often in people who have not been vaccinated against diphtheria. The films have the ability to block the lumen of the larynx, which, combined with its swelling and muscle spasm, limits the flow of air into the lungs.
Symptoms of diphtheria form:
- the presence of a white coating on the back wall of the throat, which is difficult to remove, and after its removal droplets of blood appear;
- difficulty breathing;
- dyspnea;
- a sore throat;
- loss of voice.
Catarrhal form
The catarrhal form of laryngitis is considered the easiest in terms of course and possible complications. At the same time, it is the most common form of the disease. Most often it occurs during the cold season. It is accompanied by damp weather, high air humidity, and hypothermia.
These factors accompany the development of the inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the throat and larynx, swelling of the membrane and its hyperemia occurs.
The characteristic symptoms of the disease are the following:
- dryness and burning in the throat;
- pain when talking;
- cough - first dry, later wet. With the appearance of sputum, the sore throat goes away;
- increased body temperature;
- the presence of purulent mucous exudate, which is formed due to the effusion of fluid from inflamed vessels.
Professional uniform
Occupational laryngitis develops as a result of constant overstrain of the vocal cords. They do not close completely, which causes characteristic symptoms. When examining the ligaments in a laryngoscope, redness of the vocal folds is detected; they look dull, dry, with loose edges. If not treated in a timely manner, catarrh of the larynx and trachea is possible.
Symptoms of occupational laryngitis:
- hoarseness or loss of voice;
- a sore throat;
- sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- rapid fatigue of the voice after slight straining.
Causes of chronic laryngitis
The causative agents of chronic laryngitis are:
- Various viruses. These include measles, parainfluenza, influenza and others viruses;
- Bacteria. These include: the causative agent of diphtheria, scarlet fever, whooping cough, mycobacteria, streptococci, treponema, staphylococci and others.
The main causes of chronic laryngitis in adults:
– Local hypothermia, cold drinks, irritating foods, strong and prolonged vocal strain, mouth breathing. All these signs can lead to disruption of the throat protection system. The cellular structure of the mucous membrane is damaged and chronic and subsequently acute bronchitis develops;
– Excessive contact with sick people. Whooping cough, influenza, chicken pox, other acute respiratory viral infections. The incubation period for laryngitis of infectious origin can be only a few hours. It all depends on the pathogen;
– The cause of chronic laryngitis can be infections from the paranasal sinuses with sinusitis, the mouth, and nearby areas;
– Inhalation of any irritants. These can be various chemicals, soot, dust;
– Periodic or constant tension of the vocal cords (voice loss);
– Damage to the surface of the mucous membrane of the larynx through surgery or mechanical impact (fish bone, crackers, poorly chewed food);
– Abuse of tobacco and alcoholic beverages.
Chronic laryngitis can develop as a result of gastric contents entering the larynx. This is the so-called gastroesophageal reflux. This condition occurs due to the weak function of the esophageal sphincters, which prevent the contents of the stomach from entering the esophagus, pharynx and larynx.
It is worth understanding that chronic laryngitis can change from acute laryngitis with reduced immunity, low body resistance to disease, and also in the presence of bad habits.
Diagnostics
How to treat laryngitis in adults: with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory or antiallergic drugs can only be determined after diagnosing the disease and establishing the cause of the disease.
Diagnostics should include the following main steps:
- collecting medical history and patient complaints;
- external examination of the patient;
- laboratory research;
- instrumental examination.
Laboratory examinations will provide information about the possible inflammatory process and its severity. They can also be used to make a differential diagnosis between the allergic nature of the disease, bacterial, viral or fungal.
The necessary laboratory tests are the following:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- throat culture for bacterial flora;
Instrumental diagnostic methods are used to visualize the vocal cords and pyriform openings.
The most commonly used methods are:
- laryngoscopy upper and lower;
- biopsy of mucosal areas if an oncological process is suspected;
- Ultrasound of lymph nodes and thyroid gland.
Chronic laryngitis: symptoms in adults
In a patient with chronic laryngitis, the general condition is not disturbed. There is a sore throat, as well as hoarseness and rapid fatigue of the voice. Cough with sputum is observed periodically. Symptoms may intensify if the process worsens.
Chronic laryngitis: main symptoms:
– the timbre of the voice changes;
– hoarseness;
– soreness, feeling of a foreign lump in the throat, dry mouth
- cough.
Chronic laryngitis in an adult can be in the form of a rare cough or in the form of an attack. During remission, the above symptoms may be less pronounced when compared with an exacerbation. As symptoms increase, loss of appetite and general weakness of the body are possible. To effectively begin treating chronic laryngitis in an adult, you need to consult a doctor and obtain diagnostic results.
First aid
First aid for an attack of acute laryngitis should not be delayed. The faster it is provided, the more effective its result will be.
The first aid algorithm consists of the following necessary points:
- The patient needs to be given a lot to drink. The liquid should be warm, preferably alkaline (alkaline mineral waters of Borjomi, Essentuki), but tea or plain water will also do. You can take tea with honey if you are not allergic to it.
- Take an antihistamine (diazolin, loratadine, suprastin).
- Drink an antispasmodic (no-spa, riabal, drotaverine).
- Humidify the air (hang wet towels or spray water in the room).
- Take a soda inhalation. Steam inhalation of boiled potatoes or brewed herbs also works well.
- Warm baths for feet and hands. Adding mustard seeds to warm water is also effective.
Drug treatment and antibiotic therapy depending on the form of the disease
Treatment for laryngitis depends on its cause. First, it is necessary to eliminate the causative agent of the disease, because without this the disease will recur constantly. The next step is to treat the inflammatory process of the larynx.
Treatment should be comprehensive and take into account the form of the disease. But, there is one point that is recommended for patients with any form of laryngitis. This is rest for the vocal cords, or “silence mode.”
Allergic form
How to treat laryngitis in adults if its cause is an allergic factor: with hormonal agents or sufficient antiallergic drugs, factors such as the severity of symptoms and the rate of its increase will help answer. The main rule in the treatment of this form is the elimination of the allergen. All the following are aimed at eliminating the consequences of its impact.
Drug therapy for allergic laryngitis:
1. Taking antihistamines:
- suprastin;
- citrine;
- tavegil.
2. Taking antispasmodics:
- no-shpa;
- riabal.
3. Glucocorticoids - they are prescribed for severe attacks:
- dexamethasone;
- prednisolone.
4. Sedatives:
- Valerian tincture;
- seduxen.
Soda inhalations also have good results.
Atrophic form
Treatment of atrophic laryngitis is divided into local and general. Local therapy includes alkaline-potassium and oil-alkaline inhalations, instillation of the larynx with chymotrypsin and lysine, lubricating the back of the pharynx with Lugol's solution or rosehip oil.
General treatment consists of the following points:
- use of biogenic stimulants (aloe, FIBS);
- vitamin therapy (ascorbic acid, B vitamins);
- antibiotic therapy:
- Ceftriaxone – a broad-spectrum antibiotic of the cephalosporin group. Prescribed as intramuscular or intravenous injections of 1-2 g per day. The course of treatment is 5-7 days.
- Amoxiclav is a penicillin antibiotic. It is prescribed in tablets of 250-500 g 1-2 times a day. Duration of treatment is 3-7 days.
- Levofloxacin is an antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone group. Used in the form of tablets of 500 mg 1-2 times a day for 5-7 days.
Hemorrhagic form
Treatment of the hemorrhagic form of laryngitis should be aimed at moisturizing the laryngeal mucosa and include antibacterial therapy. In this case, oil inhalations have a good effect.
For local treatment the following agents are used:
- Bioparox is a propolis-based drug that effectively relieves inflammation and destroys streptococcus and staphylococcus bacteria. Apply 2-3 injections into the throat 3-4 times a day. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Lugs is a spray with an antibacterial effect. Prescribe 1 injection 4-5 times a day for a week.
To reduce irritation of the mucous membrane, it is necessary to take antitussive medications:
- Stoptussin – 1 tablet. 3 times a day;
- Ascoril - 1 tablet. 2-4 times a day.
Hypertrophic or hyperplastic form
The hypertrophic form of the disease requires treatment with an effect on areas of hypertrophied mucosa. Sometimes drug treatment is not enough, so in some cases surgery is necessary. It consists of excision of the affected areas of the mucosa and is a prevention of laryngeal cancer.
Also, for this form of laryngitis, the following procedures are recommended:
- cauterization of hypertrophied areas with a 3-5% solution of silver nitrate;
- irrigation of the mucous membrane with a 3% solution of collargol;
- inhalation with hydrocortisone.
Fungal form
A combination of antifungal drugs and antibiotics will help both treat laryngitis in adults caused by a fungal nature and eliminate the symptoms of the pathology.
The following antifungal drugs are used:
- Nystatin – 1 tablet. 2-3 times a day;
- Levorin – 1 tablet. 3 times a day;
- Griseofulvin – 1-2 tablets. 2 times a day.
Antibiotics are also prescribed in combination with one of the antimycotic drugs:
- Azithromycin – 500 mg per day for 6 days;
- Clarithromycin - depending on the severity of the process, 250-500 mg every 12 hours for 7 days.
Diphtheria form
The diphtheria form requires mandatory hospitalization and observation by an infectious disease specialist. Due to the dangerous consequences, the patient must be given special attention.
Treatment of this form consists of the following points:
- The most effective method is the administration of anti-diphtheria antitoxic serum - the further development of complications depends on the timing of its administration.
- Macrolide antibiotic: Azithromycin, Clarithromycin.
- Vitamin therapy: vitamin C, B1, B12, PP.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Nimesil, Ibuprofen.
Catarrhal form
The catarrhal form responds well to treatment. It should include a local antiseptic, anti-inflammatory agent and antitussive drugs. A local antiseptic relieves inflammation and soothes the throat.
The following drugs are recommended:
- Chlorophyllipt – exists in the form of spray and tablets. Take 1 tablet. or 1 injection 4-6 times a day.
- Hexasprey – 1-2 injections 3-4 times a day.
Antitussives are used only in the absence of sputum:
- Sinekod – 15 ml 3-4 times a day.
- Stoptussin – 1 tablet. 3 times a day.
Treatment of laryngitis at home
If the disease has an uncomplicated course and the patient does not develop laryngeal stenosis, then treatment can be carried out at home.
Difficulty breathing requires hospitalization. Patients with various complications of infection, for example, inflammation of the bronchi, also require special attention. In any case, before starting treatment you should consult a specialist.
- Antiseptic treatment of the throat.
First of all, you should take care of the antiseptic treatment of the throat. For this purpose, special sprays and lozenges are used, for example AntiAngin, Strepsils, Sage tablets.
- Caress your throat more often.
Gargling can increase the effectiveness of treatment. For this purpose, drugs such as Miramistin and Furacilin are used. In addition to pharmaceutical solutions, you can supplement therapy with homemade products. A mixture of salt and soda disinfects the surface of the oropharynx well. For a glass of water you will need a teaspoon of each bulk substance. You can enhance the effect with iodine. It is added in the amount of 2 drops per glass of water.
- Herbs for gargling.
In the treatment of laryngitis, alcoholic tinctures of medicinal herbs are used. They can be purchased at the pharmacy. It is recommended to use tincture of calendula, St. John's wort and sage. To do this, pour 2 tablespoons of herbal tincture into a glass of warm boiled water and gargle the sore throat with this mixture.
When laryngitis is non-infectious in nature, you can use a decoction based on oak bark, chamomile, coltsfoot and burdock. To prepare it, take 20 g of herb, add 200 ml of boiling water and boil for 10 minutes. Then the solution is cooled, filtered and used for its intended purpose.
The throat needs to be treated at least 4-6 times. When the disease is acute, rinse it 8-10 times a day. Treatment should continue for at least a week.
- Pharmacy sprays.
In addition, sprays and aerosols can be purchased at the pharmacy.
Sprays and aerosols that can be purchased at a pharmacy for the treatment of laryngitis:
- Lugol.
- Inhalipt.
- Tantum Verde.
- Hexoral.
- Kamenton. Sage lozenges from Natur product
- Inhalations for laryngitis
. Inhalations help relieve inflammation, coat a sore throat and soften it. To cope with the disease as soon as possible, you can brew fennel, mint, dill and breathe in their vapors.
- Inhalations with dill seeds.
Pour two tablespoons of dill seeds into 2 cups of boiling water and breathe in its vapor until the water cools down.
- Inhalations with honey.
A tablespoon of honey and 2 teaspoons of propolis are poured into a liter of boiling water and the healing vapors are inhaled for 10 minutes.
- Inhalations with garlic and herbs.
A paste of 2 cloves of garlic is mixed with 2 teaspoons of mint and eucalyptus and poured with boiling water. Breathe medicinal vapors for at least 10 minutes.
Lugol is prohibited for use in the treatment of children under 5 years of age, as well as for persons allergic to iodine.
Inhalations are carried out 2 to 4 times a day for a week. Procedure duration 20 minutes
After heat treatment of the throat, you need to refrain from eating for an hour. In addition to steam inhalations for laryngitis, inhalations can be performed using a nebulizer. The device is filled with saline solution mixed with drugs such as: ACC, Lazolvan, Ambrohexal, Ambrobene.
Professional uniform
In the treatment of the professional form of laryngitis, the “silence regime” plays an important role. It must be observed as often as possible between periods of stress for professional reasons. Oil-alkaline inhalations and physiotherapeutic procedures are also effective.
To relieve pain, it is recommended to take anti-inflammatory drugs, sprays and special lozenges:
- Isla-moos – it contains Icelandic moss, which is effective for hoarseness, dry throat and dry cough;
- Isla-mint – has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Broncho-veda is a homeopathic herbal medicine that affects cough and sore throat.
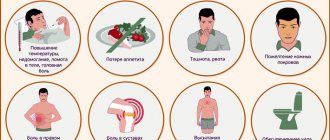
Symptoms of laryngitis
The onset of the disease is usually manifested by weakness, lethargy, and loss of appetite. Laryngitis is often accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Then a sore and sore throat occurs, the voice becomes hoarse and its timbre changes. Sometimes a person can only speak in a whisper.
The cough with laryngitis is quite specific, it resembles a dog barking. Attacks can occur during the day, but they are especially annoying at night, when a person assumes a horizontal position. During the recovery stage, the cough turns into a wet one.
The disease can be acute, when its symptoms are pronounced and disappear within a week after adequate treatment, or chronic. In the second case, hoarseness and cough occur periodically.
Aloe juice is used for medicinal purposes. The plant increases the resistance of the mucous membranes of the oropharynx to damage and accelerates regeneration.
Treatment is usually carried out at home. Adults are hospitalized only if laryngitis develops against the background of other chronic diseases or leads to complications.
Instillations of the larynx
Laryngeal instillations for laryngitis are used quite rarely, but this is due to the difficulties of the procedure itself, and does not mean that it is ineffective. The manipulation is carried out only by an educated specialist using a special laryngeal syringe and a mirror. The procedure is non-contact, and for complete healing it takes from 3 to 10 sessions.
The most common means are:
- collargol solution – is especially effective in the case of hypertrophic laryngitis, but in other cases it also has antimicrobial, antiviral and antimycotic effects;
- chlorhexidine - acts as a local anesthetic with an antimicrobial effect;
- Lugol's solution.
Thermotherapy
Heat therapy is one of the simplest and most important methods of combating the disease. In the early stages of the disease, dry heat on the neck area is recommended, sometimes a regular scarf is enough. Applications with warm sand or salt to the neck area and warm compresses are also used.
Heat for laryngitis is also used internally. During an exacerbation, you should drink only warm liquids, since hot or cold liquids can irritate the mucous membrane and contribute to the continuation of the disease. Warm herbal teas with honey, raspberries, and linden are recommended.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is aimed at reducing swelling and inflammation of the larynx. The following physiotherapeutic treatment methods are prescribed:
- ozokerite therapy;
- paraffin therapy;
- laser treatment;
- amplipulse therapy;
- FUF irradiation.
Rinse and inhalation
Laryngitis in the early stages quickly regresses when gargling with different solutions:
- rotokan;
- soda;
- potassium iodide.
Manipulations should be carried out 3-4 times a day, the effect will be better when alternating solutions. Inhalation of drugs is one of the best methods of treatment, since in this case the drugs act locally. Inhalations are effective for various forms of the disease.
The most commonly used means are:
- Hydrocortisone - has an anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effect, relieves swelling of the larynx and spasm of smooth muscles, and is most effective in the treatment of allergic laryngitis.
- Soda buffer – relieves swelling and has a mucolytic effect.
- Lorde - has an expectorant and antiseptic effect.
Treatment with honey
There are many different “grandmother’s” recipes for treating laryngitis with honey, for example:
- Pour one teaspoon of honey into a glass of boiling water and cook over low heat for a minute. After this, cool a little and gargle 2-3 times a day.
- Boil water and add a tablespoon of honey. Place a rubber tube on the kettle and carefully inhale the vapors of honey and water for 15 minutes.
- Take 2 tablespoons of black elderberry and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Let the berries sit for 40 minutes, then strain and add a tablespoon of honey. Take the drug 0.5 cups warm 2-3 times a day.
- Dissolve a tablespoon of honey in a glass of hot milk and take it day and evening until the sore throat goes away.
- Pour a glass of dried viburnum berries with a liter of boiled water and simmer for 10 minutes, then let it brew for at least an hour. Next, add 3 tablespoons of bee honey and stir it well until completely dissolved. Take half a glass 3-4 times a day.
- Mix freshly prepared horseradish juice with bee honey, maintaining a 1:1 ratio, and take a tablespoon with warm water before going to bed.
Traditional recipes for laryngitis
Traditional medicine can answer how to treat laryngitis in adults at home without using medications. There are many recipes to combat laryngitis, but they must be used from the very beginning of the disease or in complex therapy in the later stages.
The most common and well-known methods are gargling with soda or salt. To prepare such a solution, add 1 tsp. salt or soda in 1 glass of warm water, stir until the substance is completely dissolved and gargle with the resulting mixture throughout the day.
But there are other effective recipes:
- Medicinal juice – take equal quantities of raw beets, carrots and potatoes. Squeeze juice from vegetables and strain. Use as a rinse 4-5 times a day.
- Carrot decoction with milk - take 1 carrot and 200 ml of milk. Cook over low heat for 20 minutes, then remove, take out the carrots and leave to cool. Gargle with warm milk 4-5 times a day.
Traditional medicine against illness
Laryngitis is considered one of the most complex diseases of the upper respiratory tract, as it can lead to complete loss of voice, atrophy of the vocal apparatus, stenosis, scar deformation, as well as malignant or benign tumors of the larynx.
Important to know: How to treat acute laryngitis
Therefore, this pathology should be treated only in accordance with the doctor’s instructions, combining traditional therapy, a healthy lifestyle and diet.
For laryngitis, treatment at home is quite affordable.
Traditional methods of treatment involve the use of natural ingredients; in most cases they are safe and effective, therefore they can be used as additional therapy and prevention of laryngitis.
To avoid complications and possible allergic reactions, you should consult a doctor before starting treatment.
Rinse
The easiest way to treat laryngitis is to gargle. For laryngitis, folk remedies for rinsing are a solution of soda (a spoonful of soda in a glass of warm water) and sea salt. The procedure should be used at least 4 times a day.
For herbal rinses, you can use nettle, sage, chamomile and calamus roots.
To relieve the symptoms of acute laryngitis, pour two teaspoons of any herb into a glass of boiling water and leave for a couple of hours, after which it is heated and gargled at least 5 times a day.
Calamus roots can be combined with chamomile and cinquefoil flowers, pour a tablespoon of the mixture with hot boiled water, leave for a while, then gargle every 4 hours.
For rinsing with laryngitis, folk remedies can use potato or beet juice diluted with water, as well as milk, in which carrots must be boiled in advance.
It is recommended to perform the procedure at least five times a day.
Inhalations
A folk remedy such as inhalation will also help cure laryngitis.
Inhalations in combination with rinses significantly speed up the healing process, and the procedure can be performed not only on the basis of medications or saline solution, but also on the basis of traditional medicine.
Important to know: Treatment methods for allergic laryngitis
Steam inhalation can be done at home using a narrow-necked container or a regular kettle.
You can breathe steam through a long paper funnel 15 minutes after the liquid boils, as hot air can further intensify the symptoms of laryngitis.
For chronic laryngitis, inhalation of an alkaline solution is considered effective, for which you will need a teaspoon of soda dissolved in a glass of warm water.
To facilitate the discharge of sputum, inhalations are made using non-carbonated mineral water.
To achieve greater results, you can combine an alkaline solution with a herbal decoction, for which the same plants are used as for rinsing.
It is recommended to add a few drops of menthol or eucalyptus oil to solutions for inhalation. Each procedure should last no longer than 10 minutes with a frequency of at least 3 times a day.
Honey therapy
Natural honey is considered a proven and effective remedy for diseases of the respiratory system, but is contraindicated in patients with an allergic reaction to bee products.
In order to alleviate the symptoms of the disease, you need to slowly dissolve one spoon of honey in your mouth several times a day, you can also combine it with other ingredients:
- effectively treat laryngitis with a mixture of honey and lemon juice in a 2:1 ratio. Take a tablespoon of the mixture every hour during the day;
- 300 ml of carrot juice and two tablespoons of honey, take a tablespoon every 4 hours;
- half a tablespoon of honey and chamomile decoction (or warm milk), drink at night and wrap your throat with a woolen scarf;
- half a liter of aloe juice and 200 grams of honey, take a teaspoon three times a day.
Thus, laryngitis can be successfully treated with folk remedies, but under the supervision of a doctor.
Nutrition for laryngitis in adults
Nutrition for laryngitis should comply with the following rules:
- food should be warm (neither hot nor cold!);
- It is necessary to exclude spices and seasonings from the diet;
- Rough food can also injure the mucous membrane, so soups, cereals, and purees are recommended;
- exclude alcohol;
- exclude carbonated drinks;
- fried and fatty foods can also negatively affect the laryngeal mucosa, so you should avoid them.
Laryngitis will worsen less often if you adhere to these simple nutritional rules, and the question will arise less often: how to treat it in an adult.
Chronic laryngitis: treatment in adults
How to treat chronic laryngitis in adults? Treatment of the disease involves a gentle regimen. Patients need rest. It is necessary to eliminate factors that contribute to increased inflammation: avoidance of spicy, cold, hot foods, as well as avoidance of smoking and alcoholic beverages.
There is a general treatment regimen for chronic laryngitis:
– It is necessary to eliminate possible causes of laryngitis. Relieve stress on the larynx and vocal cords;
– Avoid foods that irritate the mucous membranes. These can be salty and spicy foods, carbonated drinks;
– Quitting smoking and alcohol;
– Drink plenty of warm drinks. For chronic laryngitis, you can drink milk, juices, jelly, decoctions, infusions and tea.
If chronic laryngitis has developed, treatment in adults can be carried out with the following medications and therapies:
– external medications for basic treatment. These are aerosols, lozenges and dissolving tablets;
– expectorants;
– antiallergic drugs;
– antibacterial antibiotics;
– targeted antibiotics;
– antiviral drugs;
– means to improve immune defense and strengthen the general condition of the body.
Drugs that have an antibacterial effect can be prescribed for chronic laryngitis if there is confirmation of the bacterial nature of the disease.
In addition, treatment of chronic laryngitis in adults is carried out using effective physiotherapeutic methods.
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis of the disease depends on its form and treatment. In most cases, it is favorable, but it can become chronic. The most dangerous are allergic and diphtheria laryngitis. If the necessary specialized assistance is not provided for these forms, the prognosis worsens, laryngeal stenosis intensifies, edema progresses, which leads to adverse consequences.
| Local | System |
|
|
Laryngitis is a common illness in adults and children, and its treatment usually does not require much effort. But sometimes the disease progresses, becomes complicated and cannot be treated with ordinary lozenges for a sore throat. If you adhere to proper nutrition, voice mode and seek qualified help in a timely manner, then the question of how to treat laryngitis will cease to worry.
Article design: Mila Friedan