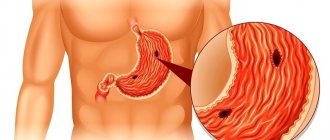
What is an enlarged liver
Hepatomegaly - as liver enlargement is officially called in the medical field - is not a disease, but is one of the characteristic symptoms indicating problems of the hepatobiliary system. The danger of an enlarged liver is not only in the disruption of its function and the digestion process, but also in the fact that it can be a sign of diseases of organs and systems not related to the gastrointestinal tract - the heart, blood. It is important to stop liver bloating (this is how the patient perceives the problem) at the initial stage, since it has many serious consequences:
- liver failure, resulting in death;
- the development of a disease, the symptom of which is an enlarged liver;
- formation of low-quality tumors;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hepatocarcinoma.
What herbs help with an enlarged liver?
Herbal medicine, when increasing the parenchyma, accelerates the process of restoring the normal size of the organ. For infusions and decoctions, pharmaceutical preparations, choleretic, anti-inflammatory herbs, and stimulators of hepatocyte regeneration are used. Plant components should be consumed in small portions. For a glass of boiling water you need 1 teaspoon of dry mixture. What herbs help an enlarged liver:
- Milk thistle, based on its components, produces hepatoprotectors;
- Potentilla erecta or Kalgan is used in pharmacology as an antimicrobial and tanning agent;
- Erva woolly or Paul fell improves the permeability of liver cells, promotes their restoration, and is often included in the treatment complex when the organ is enlarged;
- Volodushka has anti-inflammatory properties and relieves fever well;
- Immortelle or Tsmin is rich in flavonoids that cleanse the parenchyma.
Reasons for the increase
A pathological change in the size of the liver towards enlargement can be associated with liver diseases, circulatory problems, and some infections - only a doctor will make an accurate diagnosis based on the results of several diagnostic tests. The main causes of an enlarged liver by doctors include:
- Tumors – adenoma, carcinoma (primary), metastatic cancer, cysts (polycystic), focal nodular hyperplasia. Mostly in this situation, the right lobe of the liver or the left (not the entire organ) is enlarged.
- Inflammatory processes - cirrhosis, hepatitis of drug etiology or viral.
- Infiltrative processes - hepatosis, steatosis (fatty degeneration), leukemia, lymphoma, amyloidosis, tuberculous or sarcoid hepatitis (less often due to cytomegalovirus), hemochromatosis.
- Hereditary factors – Gaucher disease, congenital metabolic problems.
- Toxin damage – due to alcohol addiction or drug treatment.
- Circulatory problems - failure of the right heart, blockage of the hepatic veins.
- Helminthiasis.
- Viral/bacterial infections affecting the hepatobiliary system.
- Gallstone disease, lipid metabolism disorder.
A separate and very important point is an enlarged liver in a child: if this happened to a newborn (and the parents noticed it, and not the doctor during the examination), the cause may lie in jaundice. This disease is very common among infants and does not require treatment, since all symptoms go away on their own, and the cause of its development is considered to be:
- birth injuries;
- maternal endocrine system disorders (especially diabetes).
One should not be afraid of an enlarged liver in preschool children: pediatricians consider this a natural phenomenon associated with the development of the body. If the organ can be felt beyond the ribs to a length of 1-2 cm, this is not dangerous and will go away as the child grows older. If the size of the liver does not change and exceeds the established norm in a child over 7 years old, accompanied by additional symptoms of internal disorders (nausea, fever, yellowness of the mucous membranes and skin, the appearance of rashes, weight loss), the reasons may lie in:
- presence of metastases;
- pathologies of metabolic processes;
- congenital TORCH infections;
- toxic/drug-induced liver damage;
- diseases of the biliary tract;
- blockage of the bile ducts.
Reasons for deviations from the norm
The cause of an enlarged liver depends on the preferred treatment method. In fact, hepatomegaly is not a diagnosis yet. Therefore, before providing any assistance, it is necessary to determine its etiology.
Often the reason for this deviation is the following disturbances in the functioning of the body:
- fatty hepatosis,
- hepatitis,
- early stage cirrhosis,
- metabolic disorder,
- heart failure,
- cyst,
- cancer tumor,
- damage to hepatocytes.
The right lobe of the liver is most susceptible to enlargement due to severe stress. As for the left side, it most often suffers due to problems of the pancreas, which has a direct impact on the functioning of this lobe. Due to the diffuse increase in the size of the organ, systematic atrophy of hepatocytes occurs, after which it is replaced by fibrous tissue.
The liver enlarges smoothly; as it enlarges, it begins to put more pressure on the organs located next to it . This leads to a change in their shape and a deterioration in the human condition. Therefore, treatment should be started immediately.
How to understand that the liver is enlarged
The patient recognizes the problem mainly by unpleasant symptoms, which can also be observed when the organ is not too enlarged (when independent palpation brings almost no results). Hepatomegaly is always characterized by a feeling of discomfort in the right hypochondrium, among the unpleasant moments is a feeling of heaviness and pressure. Additionally there may be:
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes;
- changes in the color of urine and feces;
- heartburn;
- severe belching, nausea;
- increased irritability, emotional instability.
More accurate ways to detect an enlarged liver are classical methods of examining the hepatobiliary system - MRI, CT, ultrasound. With hepatomegaly along the right clavicular line, the organ is more than 12 cm in length and can be easily palpated in the left lobe of the epigastric zone. You should definitely keep track of the following points:
- presence or absence of organ prolapse;
- the presence of third-party tissues in the right hepatic quadrant;
- sensations during palpation - density of the palpated area, pain.
How to treat
To determine the list of therapeutic measures that will be taken, it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis: for this, in addition to the mentioned types of diagnostics - MRI, CT, ultrasound - a biopsy (if there is a suspicion of cancer or steatosis), and detailed blood tests can be prescribed. Additionally, the doctor will compile the patient’s complaints and, in a difficult situation, refer him to several more specialists. The treatment regimen for an enlarged liver is often discussed not only with a gastroenterologist, but with a hepatologist and infectious disease specialist. A few general points:
- Whatever the cause of an enlarged liver, one of the main points of treatment will be diet. The doctor will outline the exact dietary restrictions, but the essence of it is to spare the organ. How long you will have to stick to the diet is also discussed with a specialist, but be prepared that this stage of treatment will last for several months or years.
- The drug treatment regimen necessarily contains drugs from the category of hepatoprotectors, which have not so much a therapeutic quality as a preventive one. They are needed to support the diseased organ, but will not eliminate existing diseases.
- No cure for liver enlargement will work if the problem is advanced hepatitis: in the later stages, the only “treatment” measure is transplantation, and before that, doctors try to prevent the rapid development of complications.
Diet
The key nutritional goals for a person with an enlarged liver are to reduce the load on the diseased organ and restore its functions, especially the outflow of bile. Whatever diseases cause hepatomegaly, fasting is not allowed - this is no less dangerous for the liver than excessive food consumption. Any diet for liver enlargement in adults and children requires compliance with several basic rules:
- Fractional nutrition - small portions, frequent meals: this way you will protect the organ from overload and stimulate the frequent release of bile. It is advisable to eat at least 5 times a day (snacks count), and some patients should maintain an interval between meals of no more than 2 hours: the exact figure depends on lifestyle.
- Reducing the amount of protein in the diet - this is especially important for people suffering from cirrhosis, as they are at high risk of developing hepatic coma due to increased levels of ammonia in the blood.
- Refusal of spicy and fatty foods are the main sources of stress for the hepatobiliary system, due to which the enlarged liver can continue to grow in size.
The most used nutritional option by gastroenterologists for patients with liver diseases is treatment table number 5 (according to Pevzner), but before starting treatment, you should consult with a specialist. Not all diagnoses can be treated with a universal menu. If we focus on table number 5, then when treating hepatomegaly the following products are prohibited:
- baked goods, puff pastry products;
- dairy and fermented milk group with a fat content percentage above 5%;
- sauces;
- fatty meat (pork, lamb);
- fatty fish (sturgeon, trout, salmon, etc.);
- egg yolks;
- strong meat/fish broths;
- fast food, semi-finished products, sausages;
- canned food;
- legumes;
- sorrel, spinach;
- cocoa and its derivatives;
- confectionery;
- refined sugar;
- coffee;
- carbonated drinks.
The basis of the diet during treatment for hepatomegaly is vegetables, preferably heat-treated, fruits, and herbs. Cereals, vegetable and milk soups, river fish, dietary meat (chicken, turkey, veal) are allowed. Milk derivatives are taken low-fat, in small quantities. Every day you are allowed to eat 1 whole egg, prepare compotes with dried fruits, but without sugar. Weak tea, freshly squeezed vegetable and fruit juices, non-acidic berries, honey, and marmalade are not prohibited. Rarely is butter or olive oil added to prepared dishes.
- How to change tariff on Beeline
- Stearic acid - properties and harm. Application of Stearic acid in cosmetology
- Isofra - instructions for use for children and adults
Sample menu for the week
The diet of a person with an enlarged liver should include boiled or baked pumpkin and beets, of which 150-200 g are eaten daily (maximum amount - 1 kg). Don’t give up cranberry juices/fruit drinks or rosehip decoction - they contain a large amount of vitamins and nutrients. While an enlarged liver is being treated, it is advisable for the patient to adhere to the following menu:
| Breakfast | Snack | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner | |
| Monday | Steamed cheesecakes, weak tea | Persimmon (2-3 pcs.) | Milk soup with noodles | Glass of pumpkin juice | Steamed chicken breast with orange |
| Tuesday | Oatmeal with banana | Dried fruit compote without sugar | Steamed turkey soufflé | Flourless cottage cheese casserole | Vegetable stew |
| Wednesday | Cottage cheese (2-5%) with a spoon of 10% sour cream and herbs | Baked pumpkin (200 g), dried bran bread | Pilaf without meat | Vegetable salad with a spoon of olive oil | White fish soufflé, steamed green beans |
| Thursday | Buckwheat porridge with prunes | Currant jelly | Vegetable soup with brown rice | Applesauce with dried apricots | Steamed turkey fillet with vegetable salad dressed with lemon juice |
| Friday | Rice porridge with raisins and honey | Baked pear with cottage cheese | Pasta with vegetable cutlets | Boiled egg, bell pepper | Steamed cod meatballs with carrots |
| Saturday | Oatmeal with a handful of almonds and an apple | Fresh pumpkin, zucchini and carrots | Boiled chicken breast without salt with vegetable salad | Baked apple with cinnamon | Vegetable casserole with sour cream and herbs |
| Sunday | Egg white omelette with cucumber | Apple juice, grain bread | Vegetarian borscht | A glass of kefir or natural yogurt | Stewed veal with boiled beets |
How and what to treat correctly
The course of treatment for liver enlargement should be prescribed by a doctor. Additional diseases and the degree of development of pathology play an important role. If there are serious complications and disruption of important systems, surgical intervention may be necessary.
The duration of treatment directly depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and the underlying disease that provoked hepatomegaly. On average, this process takes several months. If there are complications, the prognosis is alarming. The liver may lose its ability to perform some functions.
Medicines
Drugs for the treatment of liver enlargement are prescribed individually
During therapy, it is important to eliminate or stop the development of the disease that caused hepatomegaly. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable
Taking the wrong medications will not only not get rid of the problem, but will also worsen the general condition of the body.
- drugs with anti-inflammatory effect (Allohol, Essentiale);
- medications with restorative properties (Gepamerz, Hepatrin);
- preparations with milk thistle extract (Legalon);
- hepatoprotectors (Essliver Forte);
- homeopathic medicines (Galstena);
- herbal preparations (Ovesol, Gepabene);
- vitamins B and E in capsules.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine recipes are recommended to be used as an auxiliary method in the treatment of liver enlargement. It is better to discuss folk remedies with your doctor. Natural components can improve the functioning of internal organs and improve the general condition of the body, but they cannot replace medical procedures or medications.
Examples of folk remedies:
Medicinal herbs
Medicinal herbs help speed up the treatment process and normalize liver function. Some of them improve the flow of bile and remove harmful toxins from the body. Herbs can be added to salads or used to make infusions. For a glass of boiling water you will need one teaspoon of dry mixture. Herbs can be combined with each other in one decoction.
- young lady;
- roots;
Medical nutrition
If the liver is enlarged, it is imperative to exclude foods that can aggravate the condition from the patient’s diet. These include legumes, radishes, spinach, radishes, sorrel, peppers and mustard. It is not recommended to eat sausages, baked goods, white bread, spicy and fatty foods. Confectionery products, chocolate, alcoholic and carbonated drinks are also excluded from the diet. You should not eat lamb, goose and liver.
The menu must include the following food products:
- soups with added cereals;
- lean meat;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- cauliflower;
- pumpkin;
- zucchini;
- carrot;
- grape;
- apples;
- lemon;
The main feature of the diet for liver enlargement is compliance with the rules of fractional and balanced nutrition. The body must receive a sufficient amount of vitamins, proteins, fats and carbohydrates. It is recommended to completely exclude harmful components. The menu should not contain pickled, smoked, salted or fried foods. Such categories of products negatively affect not only the liver, but also the digestive system as a whole. Dishes should be prepared by boiling or steaming.
Sample menu for the day:
- breakfast – rice porridge with milk, tea with honey;
- second breakfast – apple juice, oatmeal cookies;
- lunch - vegetable soup, steamed meatballs, rosehip broth;
- afternoon snack - dried fruits poured with boiling water;
- dinner – boiled fish with boiled carrots;
- before bed – a glass of kefir.
Some diseases that are accompanied by liver enlargement can only be treated with special medical procedures. You cannot ignore their symptoms or self-medicate. In addition, by following the rules of a healthy diet and an active lifestyle, you can prevent the development of many pathologies. The liver plays an important role in the body. If there are malfunctions in the functioning of this organ, the functioning of other systems is disrupted.
If the liver is enlarged, you cannot ignore the symptoms and neglect the treatment of the pathology
It is important to undergo a full examination as soon as possible and identify the cause of the development of hepatomegaly. It is not worthwhile to carry out therapy only with medicinal herbs or folk recipes
Such treatment may alleviate symptoms, but will not get rid of the underlying disease.
- self-medicate;
- prematurely interrupt the course of treatment;
- independently select medications for treatment;
- neglect the rules of dietary nutrition;
- eat prohibited foods;
- abuse alcohol;
- ignore signs of exacerbation of the disease.
Medicines
The selection of medications that will be used to treat an enlarged liver is carried out exclusively with a doctor. Most patients are prescribed hepatoprotectors, designed to protect the diseased organ, normalize functioning, and stop further cell changes. In addition to them, the following may be written:
- Enzyme medicines - tablets, capsules, which compensate for the lack of digestive enzymes, are especially important for pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, and pancreatic insufficiency.
- Choleretic drugs – stimulate the flow of bile.
- Antiviral drugs - make sense for viral hepatitis, but only in the early stages (the probability of cure is 85%).
- Glucocorticosteroids - used in the later stages of cirrhosis as anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Diuretics are prescribed in the presence of ascites (when fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity) and are absolutely contraindicated in the treatment of advanced stage cirrhosis, when there is a risk of hepatic coma.
Hepatoprotectors
Medicines aimed at protecting the liver often have a natural composition (mostly herbal) or belong to homeopathic medicines, so the main contraindications to them are hypersensitivity, and allergic reactions are side effects. The most effective hepatoprotectors:
- Gepabene - capsules with milk thistle and fume powder, have a choleretic effect, prescribed for adults, 1 piece. before meals 3 times a day. The duration of the course of treatment is determined by the doctor. Effective for dyskinesia, hepatitis and toxic lesions, well tolerated, not prescribed for acute diseases of the gallbladder.
- Ovesol is a combination preparation of turmeric, immortelle, mint and oats. It has 2 release forms - tablets and solution. Taken 2 times a day, 15-50 drops or 1 tablet before meals. The treatment lasts a month, no adverse reactions have been identified. Contraindication is bending of the gallbladder.
- Karsil is a drug based on milk thistle fruits, a safe food additive that protects against intoxication and restores liver cells. Well tolerated, but may cause diarrhea. Take 1 tablet with food (do not chew) 3 times a day, treatment lasts 3-4 weeks.
- Heptral is a potent medicine prescribed for cirrhosis, steatosis, fibrosis, hepatosis, and drug intoxication of the liver. Works on admetionine, has neuroprotective, antioxidant, antidepressant properties. It is prohibited for children, pregnant women and lactating women; it has a large number of side effects. Take tablets between main meals, in the first half of the day. The dose is prescribed by the doctor.
Ancillary drugs
In the treatment of hepatomegaly, enzyme and choleretic drugs play an important role, one of which is Allochol. It is of plant origin: it consists of nettle and garlic extracts, supplemented with activated carbon and animal bile. Allochol is prescribed for hepatitis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, dyskinesia of the gallbladder, cholelithiasis. It improves the function of the organs of the hepatobiliary system, improves the process of bile secretion. Key points:
- Principle of administration: after meals, for a course of 4 to 8 weeks. Dosage for adults – 1-2 tablets up to 4 times a day for the acute stage of the disease and 1 tablet up to 3 times a day for the chronic stage.
- Side effects: heartburn, belching, diarrhea, allergic reactions.
- Contraindications: acute stages of hepatitis, steatosis, pancreatitis, entercolitis, gastric ulcer, obstructive jaundice, large gallstones.
Mezim - prescribed for replacement therapy for pancreatic enzyme deficiency, works on pancreatin. It is safe, no cases of overdose have been recorded, but the tablet form is not used in children under 3 years of age. Can be used for long-term treatment (more than a year). Key points from the instructions:
- Direction of administration: with or after meals, washing down the tablet with water (100-150 ml). Adults are prescribed 1-2 tablets, children over 7 years old - 1 tablet. The daily dose for an adult patient is 4 tablets.
- Side effects: well tolerated, can provoke allergic reactions and constipation.
- Contraindications: exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis, hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Folk remedies
To speed up the elimination of toxins, prevent deterioration of well-being and protect the liver, you can add traditional medicine recipes to the main course of treatment. They will not give the same therapeutic effect as medications; they are more effective in the initial stages than in the latter, but with an integrated approach they make sense. The most effective recipes:
- Oatmeal broth - rinse a glass of oats, pour 1 liter of cold water. Bring to a boil in a small, thick-walled saucepan and simmer for 40 minutes. on low heat. Wrap in a blanket for 6 hours. Drink 50 ml before main meals for a month.
- Mix 1/4 tsp. turmeric with 1 tsp. honey, pour a glass of hot (not boiling water!) water. Stir and drink before meals. Take 4 times a day for 2 weeks.
Herbs
There are a large number of herbal infusions that help to gently restore the functions of the hepatobiliary system, stop degenerative processes, and normalize venous circulation. The following recipes are especially valued in the treatment of hepatomegaly:
- Milk thistle powder (meal) – consume 1 tsp. with each main meal, chewing thoroughly and drinking warm water. The course of treatment is a month.
- A collection of celandine, calendula, coltsfoot and St. John's wort (1:1:1:1) is taken in the amount of 2 tbsp. l., pour 500 ml of boiling water and leave for an hour. Take half a glass 20 minutes before meals. The frequency of administration is 3 times a day, the course of treatment is 4 weeks.
- Mix mint and St. John's wort leaves, motherwort herb and immortelle flowers 1:1:1:1, take 2 tbsp. l. received fee. Boil in 0.5 liters of water. Filter, drink 50 ml before meals. The course of treatment is a month.
Prevention
To prevent hepatomegaly, it is important to monitor your body weight so that excess weight does not occur: a diet is not necessary if you are not obese, but it is worth monitoring your diet. If the liver is enlarged, but the doctor does not see any serious pathologies, the main treatment measure becomes the prevention of further diseases. For this purpose, periodic courses of taking herbal hepatoprotectors are prescribed and the lifestyle is revised:
- introduce regular physical activity into your schedule;
- normalize work and rest schedules;
- eliminate alcohol and nicotine;
- minimize the number of stressful situations.
Diet for liver enlargement
The traditional way to correct hepatomegaly is diet. Doctors advise patients to adhere to the nutritional principles described in table menu No. 5. If you follow all the recommendations, recovery will come much faster. The basic rule is to use dishes prepared by a certain method - usually steaming or boiling.
The diet must include:
- soups based on vegetable broths;
- fresh, boiled, baked fruits and vegetables;
- fish and lean meat;
- dairy products and honey;
- oat jelly;
- cereals;
- sauerkraut.
You should definitely exclude unhealthy foods from the menu, and also limit the consumption of tomatoes, eggs, butter and cheeses. Hepatomegaly is an unpleasant companion to many diseases, but with the right approach to therapy, this condition can be quickly eliminated.
Often, patients themselves select suitable folk remedies for themselves if the liver is enlarged. But only a doctor should give recommendations on what to do and what methods to use in treatment.
Source