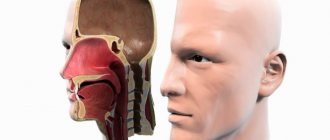
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. Almost always it appears due to a repeated deep runny nose or cold that was poorly and unfairly treated. But, besides colds and runny nose, another reason is neglected teeth, especially the upper ones. The nose becomes stuffy and mucus begins to accumulate inside. Then pus begins to come out.
In the acute course of the disease, the thin mucous membrane covering the maxillary sinuses becomes inflamed. There is also a negative effect on the blood vessels located in this area, as well as on the connective tissue. When sinusitis passes into the chronic stage, damage to the bone walls of the maxillary sinuses and submucosa is observed. People of any age category are susceptible to sinusitis. This disease develops regardless of the gender of patients.
Reasons for the development of sinusitis
The reasons for the development of the disease include:
- trauma to the nasal mucosa;
- advanced form of acute respiratory disease (acute respiratory disease);
- contact with the nasal mucosa of pathogenic bacteria or viruses;
- damage to the upper teeth by caries;
- hypothermia of the body;
- disorders of the immune system;
- mechanical damage to the nasal septum;
- allergy;
- disruption of the secretory glands;
- regular use of vasoconstrictor drugs.
Main forms and symptoms
Let us recall that the nasal cavity communicates with other cavities (sinuses) located in the bones of the facial skull. These are the sinuses of the upper jaw, frontal and sphenoid bones, cells of the ethmoid labyrinth. Sinusitis is the most common type of sinusitis. The pathology is based on inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sinuses, which are projected on both sides of the external nose.
What causes the disease and what are its symptoms?
- The viral form is considered the mildest. There is an opinion that sinusitis is a complication of a runny nose. In fact, the disease begins, as a rule, already when the virus infects the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, almost immediately entering the maxillary sinuses. With good immunity and the use of simple treatments, viral sinusitis, as a symptom of a cold, resolves in 3-5 days. This form of the disease is characterized by: clear liquid discharge from the nose, nasal congestion, and possible fever.
- With bacterial sinusitis, nasal discharge is thick, yellow-green in color, bursting pain in the nose area may occur, and swelling of the lower eyelid on the side of the affected sinus is possible. The headache intensifies when lowering the head or sudden movements. The temperature is not lower than 38 ⁰C, symptoms of intoxication of the body are expressed: general malaise, weakness, pain in joints and muscles.
- Allergic sinusitis is caused by swelling of the mucous membrane lining the maxillary sinuses as a result of exposure to an allergen. As a rule, both sinuses are affected, the discharge is clear and liquid, frequent sneezing and no signs of intoxication are characteristic. Sometimes the seasonal nature of the disease is noted.
What is sinusitis?
Sinusitis is an inflammation that occurs in the area of the nasal sinuses with the subsequent accumulation of pus in them. The disease causes a lot of discomfort to a person, in particular, the temperature rises, severe headaches occur, and signs of intoxication are also observed.
There are such types of sinusitis as:
- Catarrhal. It is rarely diagnosed in adults. Its signs include a slight increase in body temperature, lethargy, weakness, and lack of appetite. In patients with catarrhal sinusitis, signs of intoxication are revealed and performance decreases.
- Double-sided. The disease is accompanied by symptoms such as fever, headaches, congestion and severe mucus discharge from the nose, and lacrimation. Performance decreases, lethargy and sleep disturbances are noted.
- Chronic. This form of the disease develops when acute inflammation is treated incorrectly or untimely. In this case, the symptoms of sinusitis in adults are blurred; a slight runny nose and nasal congestion may occur. Possible lethargy, apathy, and disability. In case of relapse, the patient experiences the same symptoms as in the acute form of the disease.
- Spicy. In this case, the symptoms of the disease are pronounced. Severe headaches and pain in the sinuses, purulent mucous discharge from the nose, and swelling of the mucous membrane are observed. Also, with acute sinusitis, the temperature rises, breathing becomes difficult, and the ability to work is impaired.
Catarrhal sinusitis occurs in its mildest form, as it is a slight inflammation of the nasal mucosa, which over time leads to swelling. Bilateral sinusitis is considered a complication of the catarrhal form of the pathology, which often occurs in an acute form. If untimely and improperly treated, it can become chronic.
The polypous form of the disease is considered a consequence of allergies occurring in the acute stage and is characterized by the formation of polyps in the nasal sinuses. Depending on the type and form of the pathology, the doctor selects the appropriate therapy based on a thorough examination.
Surgical treatment of sinusitis
Puncture of the maxillary sinus
Despite a number of complications, puncture of the maxillary sinus is one of the most effective methods of treating sinusitis. The procedure has not only therapeutic, but also diagnostic significance. It allows you to assess the patency of the sinus anastomosis, as well as establish the nature of the pathological process.
If conservative treatment methods are ineffective, puncture of the maxillary sinus may be prescribed.
Indications for the operation:
- ineffectiveness of conservative methods of therapy;
- obstruction of the maxillary sinus anastomosis;
- severe condition accompanied by intense headaches and/or facial pain;
- the presence of a horizontal fluid level on CT (computed tomography).
It is prohibited to perform surgery for developmental anomalies and aplasia of the sinuses. Contraindications also include diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, and heart failure in the decompensation phase.
The procedure algorithm is quite simple. Before inserting the needle, the nasal cavity is cleaned and anesthetized with lidocaine solution (10%). The puncture is performed with a Kulikovsky needle, which is directed into the inferior nasal concha. In this place, the wall of the maxillary sinus is most pliable. After the puncture, the sinus is washed with antiseptic solutions.
Acute sinusitis is characterized by fever, profuse mucopurulent discharge from the nose, as well as other symptoms of general intoxication.
Complications of puncture include bleeding and air embolism.
Maxillary sinusotomy
Maxillary sinusotomy is a surgical method for the treatment of sinusitis, which involves opening the sinus and then evacuating its contents. Most often prescribed for odontogenic sinusitis.
The method is highly traumatic and is used only in extreme cases.
Signs of sinusitis in adults
The main symptoms of sinusitis in adults:
- severe runny nose;
- breathing problems;
- severe headaches;
- pain in the bridge of the nose;
- chills and weakness in the body.
Without proper and timely treatment, symptoms of sinusitis in adults can become chronic. In the acute course of the pathology, the main symptoms appear quite abruptly and do not go away after a week without appropriate therapy. If you notice the first signs of the disease, you need to consult a doctor for an examination and choose a therapy method.
Symptoms of acute sinusitis
At the very beginning of inflammation, an adult may only be bothered by malaise, because... During this period of the disease, only swelling of the mucous membranes of the maxillary sinus and nose occurs (without the development of purulent inflammation). However, swelling of the mucous membrane leads to a narrowing or complete closure of the opening between the maxillary sinus and the nasal cavity, which leads to disruption of the outflow of inflammatory infiltrate from the maxillary sinus and blockage of the sinus. This leads to the development of acute purulent inflammation in the sinus (sinuses).
During this period, an adult may complain of the following symptoms of acute sinusitis:
- Lethargy, weakened sense of smell, chills, loss of appetite, weakness,
- Body temperature rises to 37.5 - 39.0 degrees (sometimes up to 40 degrees),
- Increasing pain, which is initially localized near the inflamed sinus, but then can spread to the frontal, temporal, occipital regions, as well as to the area of the teeth, which can simulate their inflammation.
- A feeling of heaviness may appear in the corresponding half of the face, which is typical if only one maxillary sinus is inflamed,
- Mucus or pus may be released from the nasal passage on the side of the inflamed maxillary sinus, which is especially intensified when the head is tilted forward (Fig. 5). In the morning, you can also see traces of purulent fluid leaking from the nose on the pillow.
- With severe sinusitis, swelling of the soft tissues of the face, their redness, as well as the development of purulent inflammation in the oral cavity may also be observed.
- When pressing on the skin in the projection of the anterior wall of the sinus, pain may be felt; There may also be pain when tapping on the teeth located in the projection of the inflamed sinus (usually the 5th, 6th, 7th teeth of the upper jaw).
Symptoms of chronic sinusitis
Chronic sinusitis in adults can be either an independent form of the disease or the result of poorly treated acute sinusitis.
There are three forms of chronic sinusitis:
- Catarrhal form is characterized by an almost asymptomatic course, but sometimes patients may complain of a feeling of heaviness in a certain half of the face, periodic disturbances in nasal breathing, and some malaise at the end of the day. When examining the nose, an ENT doctor may detect cyanosis of the mucous membrane of the nasal passage. X-ray may be inconclusive, but a CT scan may show thickening of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus at the site of inflammation.
- Purulent and polypous forms - the difference between these forms is that in addition to the purulent exudate in the polypous form, so-called polyps (something like papillomas, only larger) are formed on the surface of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus. Polyps in the maxillary sinus are no different from polyps that often grow in the nasal passages, and they look the same.
Patients with these forms of chronic sinusitis complain of the following symptoms
- fatigue;
- putrid odor;
- periodic discharge of pus from the corresponding half of the nose;
- temperature 37.5 - 37.8.
Due to various reasons (hypothermia, decreased immunity, etc.), sluggish inflammation in the sinus can become acute. Those. an exacerbation of the chronic process occurs with the development of acute symptoms of inflammation, which will be identical to the symptoms of the acute form of sinusitis (described above).
Nasal discharge due to sinusitis
In most cases, sinusitis is accompanied by profuse nasal discharge. As a result of the inflammatory process, mucus, pus or blood clots accumulate in the paranasal sinuses.
The color of the discharge depends on the stage of the disease:
- White or transparent. They appear when the disease begins and have a liquid consistency. Before recovery, the discharge may become thick;
- Green. Indicate an acute form of the disease;
- Yellow or yellow-green. Indicate the presence of pus in the sinuses. They are often a sign of catarrhal sinusitis. The mucus is thick, viscous, with an unpleasant odor, and after drying it turns into crusts;
- Bloody. Observed in severe forms of the disease, which requires immediate treatment.
An untreated runny nose often leads to the development of sinusitis, so you need to pay attention to changes in the nature of nasal discharge, and if there is pus or other signs appear, you need to consult a doctor.
Symptoms of sinusitis
In order to recognize the disease and begin treatment on time, you need to know how sinusitis manifests itself.
When characteristic signs appear, we can assume the onset of inflammation in the maxillary sinuses
A combination of signs such as swelling and nasal congestion, headache and deterioration in general condition may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the maxillary sinuses.
Headache
Headache is the first sign of sinusitis in adults. As a result of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sinuses, the channels between the nasal passages and cavities are blocked, which leads to the accumulation of contents, which gradually turns into pus and creates excess pressure in the sinus area. Headache with sinusitis is bursting in nature. Where does it hurt in this case?
The initial pain syndrome is observed in the area of the eyes and bridge of the nose, gradually spreading to almost the entire face. At the initial stage of the disease it is not so pronounced. Sometimes sinusitis is indicated by aching pain in the back of the head that appears in the morning. As pus accumulates, they intensify and can be observed around the clock.
Headache is one of the leading symptoms of the disease
The pain becomes sharp and throbbing, more pronounced when bending or turning the head sharply. Short-term spasms may appear, which are localized near the root of the nose. It is also possible that it may intensify if the patient takes a horizontal position and the swelling in the sinuses increases.
In the later stages of sinusitis, the pain practically does not stop. It is difficult to control with medications. After taking painkillers, pain dulls for a short time, then returns with renewed vigor.
In the initial stages of inflammation, slight fluctuations in body temperature are usually observed. In the acute form of the disease, it can rise to 39 °C, which requires the use of antipyretic drugs.
In a small number of patients, headache occurs not only during an exacerbation of the disease, but also persists after treatment for sinusitis is completed. The reason for this may be the transition of the process to a chronic form, the presence of complications or a low individual pain threshold. In some cases, during a puncture, damage to one of the nerve bundles may occur, which leads to headaches or causes the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Nasal discharge due to sinusitis
In most cases, sinusitis is accompanied by profuse nasal discharge. As a result of the inflammatory process, mucus, pus or blood clots accumulate in the paranasal sinuses.
The color of the discharge depends on the stage of the disease:
- white or transparent . They appear when the disease begins and have a liquid consistency. Before recovery, the discharge may become thick;
- green . Indicate an acute form of the disease;
- yellow or yellow-green . Indicate the presence of pus in the sinuses. They are often a sign of catarrhal sinusitis. The mucus is thick, viscous, with an unpleasant odor, and after drying it turns into crusts;
- bloody . Observed in severe forms of the disease, which requires immediate treatment.
An untreated runny nose often leads to the development of sinusitis, so you need to pay attention to changes in the nature of nasal discharge, and if there is pus or other signs appear, you need to consult a doctor.
Fever
Often a symptom of sinusitis in adults is fever. It indicates the beginning of the inflammatory process and that the immune system has become more active against pathogenic bacteria, which caused the development of the disease.
The disease is often accompanied by an increase in body temperature
In the initial stages of inflammation, slight fluctuations in body temperature are usually observed. In the acute form of the disease, it can rise to 39 °C, which requires the use of antipyretic drugs.
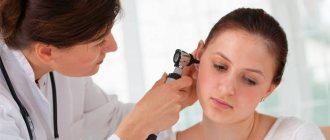
Diagnostics
For a competent specialist, establishing a diagnosis for sinusitis is usually not difficult. First of all, the doctor is based on the description of the patient’s complaints and external examination. At the initial stage of diagnosis, as a rule, swelling of the cheeks and eyelids, difficulty breathing through the nose, and pain when pressing on the face are noted.
An obligatory part of the diagnosis is examination of the nasal cavity (rhinoscopy). It allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membranes, the presence of edema and other signs.
The following methods can be used as clarifying methods:
- X-ray of the sinuses;
- puncture sampling;
- MRI;
- endoscopy;
- bacteriological analysis of nasal discharge;
- blood tests.
An immunogram is also often prescribed. And if there is a suspicion of an allergic nature of the disease, skin allergy tests are performed. It would also be useful to consult a dentist to confirm (exclude) odontogenic sinusitis.
In any case, only a specialist can establish the correct diagnosis, and timely treatment will help avoid serious complications.
What does sinusitis look like on an x-ray?
Treatment of sinusitis in adults
Symptoms of sinusitis in adults may not go away on their own. In order to avoid the development of complications, timely and effective treatment is necessary. It is not easy to get rid of the disease at home. Improper treatment in adults can lead to the inflammatory process becoming chronic and periodically exacerbating.
How to cure sinusitis in 5-7 days? In most cases, antibiotics are used in the treatment of sinusitis. Broad-spectrum agents are selected that are active against most bacteria that cause the disease. Vasoconstrictor drops are also used in the complex treatment of the disease. They allow you to restore nasal breathing and promote the outflow of contents from the maxillary sinuses. The active substance of such drops is xylometazoline or oxymetazoline.
Ready-made saline solutions (Salin, No-salt, Sodium chloride) can be prescribed for rinsing the nose. Antiseptics (Miramistin, Furacilin, Dioxidin) are also used in the treatment of sinusitis.
The following groups of drugs are used as additional treatment:
- Mucolytics: reduce the viscosity of sputum and promote its evacuation from the maxillary sinuses.
- Immunostimulants: stimulate the body’s nonspecific resistance and immunity, which speeds up recovery.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: reduce inflammation and help relieve headaches.
Signs of sinusitis in adults can be quite varied. An ENT specialist will help determine what exactly caused the headache and nasal congestion after a face-to-face consultation and relevant tests.
Treatment
In most cases, treatment of sinusitis is carried out at home, but a visit to the doctor is required. Anamnesis collection, examination, laboratory and instrumental studies will allow the doctor to establish the cause of the disease and determine the optimal set of treatment measures.
Drug therapy
If the bacterial nature of the disease is established, antibiotics cannot be avoided. Penicillin drugs, macrolides, cephalosporins, and fluoroquinolones are used. Treatment of sinusitis at home requires strict adherence to the drug regimen prescribed by the doctor. This will ensure complete destruction of the pathogen and prevent the chronic form of the disease. For allergic sinusitis, systemic antihistamines (Claritin, Zyrtec, Tavegil) are used. In addition, the following drugs are used:
- Local vasoconstrictors temporarily relieve swelling and ensure adequate drainage from the paranasal sinuses. The period of their use without harm to the mucous membrane is no more than a week.
- Pain syndrome is relieved by drugs such as Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, which also have an anti-inflammatory effect.
If conservative treatment does not help, the question of puncture arises. The procedure is performed in a clinical setting and is necessary to clarify the type of pathogen and evacuate the contents from the maxillary sinus with therapeutic manipulations.
Home and folk remedies
Speaking about how to treat sinusitis at home, it is worth mentioning the possibilities of alternative medicine (inhalations, nasal rinsing, ointments, applications). Together with medications, they will help get rid of the symptoms of infectious sinusitis in a shorter time.
Steam inhalations improve blood circulation in the area of inflammation, thin out mucus accumulations, and promote the flow of drugs from the blood. However, in acute sinusitis and especially its purulent form, heating is dangerous, since it can provoke generalization of the infectious process. Before the procedure, you must consult with your doctor.
You should breathe through your nose over a container with a decoction of medicinal herbs (bay leaf, sage, chamomile, string, celandine, calendula). You can add alcohol tincture of propolis to boiled water at the rate of 1 teaspoon per 0.5 liter of liquid, as well as a few drops of iodine. Another option is nasal breathing over freshly boiled potatoes. Inhalation procedures are carried out for 10-15 minutes, daily, for a week.
Dry heat on the area of projection of the maxillary sinuses also requires consultation with a specialist. The heat source is used:
- coarse table salt, heated in a frying pan and placed in a cotton bag;
- a hard-boiled chicken egg, wrapped in a thick napkin;
- blue lamp.
Nasal rinsing is a basic procedure for treating sinusitis at home; it alleviates the symptoms of the disease and prepares the mucous membrane for the effects of medications. To prepare solutions, use sea salt (0.5-1 teaspoon per glass of warm water), furatsilin (2 tablets), decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, celandine, sage). The procedure can be performed up to 10 times a day.
Aqualor solutions for rinsing the nose
The products of this brand are ready-to-use solutions obtained by processing natural sea water. They are placed in sealed cylinders with convenient attachments, do not contain artificial additives, and are suitable for the treatment of sinusitis during pregnancy, allergic pathology and early childhood.
The hypertonic solution Aqualor Forte draws out excess fluid from the intercellular space of the mucous membrane, which helps reduce swelling of the soft tissues. Aqualor Extra Forte has a similar effect, which, in addition to sea water, contains extracts of natural antiseptics - chamomile and aloe. All solutions help soften crusts and dissolve purulent mucous plugs in the paranasal sinuses, and also ensure restoration of the mucous membrane.
When treating allergic sinusitis, it is recommended to use Aqualor Forte to relieve swelling and isotonic Aqualor Soft to regularly cleanse the mucous membranes of allergens.
For the treatment of sinusitis in children, after consultation with the pediatrician, you can use all Aqualor products approved for this particular age of patients.
Antibiotics for sinusitis in adults in tablets
Antibiotics for sinusitis are used only after determining the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to the contained components of the product used.
Depending on the type of bacteria present, the most effective antibiotics for sinusitis may be prescribed:
- penicillin (Flemoclav, Flemoxin, Augmentin, Amoxiclav);
- macrolides (Macropen, Sumamed, Erythromycin, Fromilid);
- cephalosporins (Cefazolin, Cefuroxime, Ceftriaxone).
Penicillin helps fight most types of bacteria. Penicillin group drugs can be used in the form of tablets or injections. Cephalosporins stop the growth of pathogenic microorganisms and, moreover, they practically do not provoke side effects. Macrolides are produced mainly in the form of a suspension, which is why such drugs are suitable even for treating children.
Sinusitis can also be treated well with the help of local antibiotics, in particular, such as Isofra, Framycetin and others. They are presented in the form of drops for instillation into the nose, which can significantly slow down the growth of pathogens.
Nasal drops for sinusitis are the most effective
Liquid medications effectively destroy bacteria, make breathing easier, and compared to tablets they are good in that they do not accumulate in the blood and do not harm the intestines.
At home, treatment of sinusitis in adults can be done with the following drops:
- Sinuforte. Increase mucus production, reduce swelling and clear sinuses.
- Nazivin. Vasoconstrictor drops for sinusitis, normalizing breathing, reducing the amount of discharge.
- Isofra. Prescribed for severe forms, they contain antibiotics.
- Sialor. The spray perfectly helps with acute, allergic forms, suppressing the source of infection.
Tablets for sinusitis
There are several types of medications that can relieve symptoms and promote rapid treatment. A doctor may prescribe the following medications for sinusitis:
- Metronidazole. A medicine with antimicrobial, antiprotozoal (against protozoan pathogens) action. It quickly penetrates into single-celled organisms and leads to their death, damaging DNA.
- Ibuprofen. It relieves pain by changing the sensitivity of pain receptors, eliminates inflammatory processes, and reduces temperature.
- Bioran. An immunomodulator consisting of plant components. Strengthens the body's defenses.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers many options for treating sinusitis:
- Kalanchoe. It is necessary to wash the Kalanchoe leaves and chop them. You can use it in the same way as an onion lotion, or bury it, Kalanchoe will provoke sneezing, during which the nose and sinuses are cleared.
- Rosehip and sea buckthorn oils are instilled into the nose 6-8 times a day. This helps soften the nasal mucosa and improve the drainage of altered tissues.
- Beet. Beetroot juice has an antibacterial effect; it is enough to bury it in the nose several times a day.
- Aloe. Apply 2 drops of juice from large aloe leaves into each nostril. Aloe is known for its bactericidal properties.
- Rinse with salt water. Take half a liter of boiled water and a teaspoon of sea salt, mix thoroughly so that the solution does not damage the mucous membrane. Take any convenient vessel (bottle or teapot) and pour it into one nostril so that the water comes out freely from the other. You need to bend over and turn your head to the side. Washing should be done up to 4 times a day.
- An effective remedy for headaches that often accompany inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is cyclamen root juice. 2 drops of juice are instilled into both nostrils of the patient, while the patient is in a lying position. Five minutes later, the patient has a reaction in the form of sneezing, coughing and fever. After this procedure, pus is discharged from the patient’s nose for a whole day. Headaches are relieved and sleep patterns are normalized. There is also a pharmaceutical preparation based on the juice of cyclamen root - Sinuforte.
Decoctions of medicinal herbs are suitable for rinsing: chamomile, string, yarrow, coltsfoot; as well as an ordinary weak solution of table salt.
- Before rinsing, the nasal cavity is carefully cleaned of dried crusts, softening them with sea buckthorn oil.
- Then draw the solution into the nostril, tilt your head back, hold in this position for a while, and blow the solution out of your nose.
You can pour the solution by sucking it through one nostril and blowing your nose through the other.
Home treatment methods for sinusitis
Home treatment is often carried out by rinsing the nose with saline solutions. In the early stages of sinusitis, it is recommended to use sea salt.
To prepare the medicine, just dilute it in a glass of boiled water. Despite the fact that this medicinal component kills bacteria and viruses, you need to be aware of the following nuances:
- Do not use large amounts of salt, as there is a risk of burns during rinsing;
- There should be no grains of salt in the solution. If a precipitate is formed during the stirring process, then you should get rid of it;
- optimal water temperature – 40 degrees;
- Salt water should not be inhaled through the nose. During rinsing, it must be injected into the nasal passages using a syringe, and it should flow out from the other nostril.
Using thuja oil
This remedy improves the condition of a person suffering from diseases of the respiratory system. It can be used to treat sinusitis, sinusitis, adenoiditis and bronchial asthma.
Recommendations for instillation of the product:
- Before the procedure, it is necessary to rinse the nasal passages with saline solution. After this, 2 drops of thuja oil are instilled into each nostril. These actions should be done three times a day for six weeks;
- For 15 days, the oil is instilled three times a day, with each day gradually increasing the number of droplets to eight. This course should be repeated after a week and continued until complete recovery.
Treatment with horse chestnut
To prepare the medicine, you can use the pulp of the fruit, dry leaves and essential oil.
When deciding to use horse chestnut, you need to be prepared that there will not be an immediate effect. To achieve the desired goal, it is necessary to carry out therapeutic procedures regularly.
Horse chestnut turundas are considered very effective, since the medicine acts directly on the source of inflammation. In addition, swelling is eliminated and germs are destroyed.
To make medicinal turundas, you need to cut out small blocks of chestnut pulp that can be easily inserted into the nasal passages. Honey will help enhance the effectiveness of the method.
What will happen if left untreated?
Sinusitis is a very complex disease, and if properly treated, patients can face serious consequences:
- the appearance of swelling of the maxillary sinuses;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- violation of nasal breathing;
- strong discharge of mucus from the nose;
- accumulation of pus in the maxillary cavities, etc.
After treatment of sinusitis, some patients experience various complications:
- very often the acute form of sinusitis passes into the chronic stage, which requires longer constructive treatment;
- inflammatory processes of the bronchopulmonary system, pharyngeal tonsils and other organs develop;
- against the background of the inflammatory process, otitis media appears.
Patients who have been diagnosed with an advanced stage of sinusitis may encounter more serious complications in which various diseases appear:
- kidney;
- hearts;
- joints;
- organs of vision;
- brain, etc.
When complications go beyond the boundaries of the bronchopulmonary system and damage to other internal organs, patients may encounter sepsis. If the patient, upon identifying the primary symptoms of sinusitis, immediately goes to a medical facility and undergoes medication and physiotherapeutic treatment, he will be able to avoid any consequences and complications of this disease.