Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye. Treatment of conjunctivitis is a set of special procedures and the use of medications aimed at eliminating the causative agent of the disease and relieving its symptoms.
The disease can manifest itself as acute inflammation or a chronic process. Depending on the etiology, conjunctivitis can be contagious or non-contagious. Treatment methods are selected depending on the etiology and severity of the disease - it can be treated in a hospital in an infectious diseases or ophthalmology department, or at home, with various anti-inflammatory, desensitizing drugs, antibiotics, and traditional medicine.
Treatment should be comprehensive: the use of medicinal solutions locally and systemic medication.
Classification
Depending on the nature of the course, conjunctivitis can be acute and chronic, as well as sluggish. If you do not seek help from professionals at the first signs of the disease, the inflammatory process may subside after some time without treatment. With weakened immunity, conjunctivitis can quickly turn into an infectious form, giving purulent complications.
Experts have also identified a separate classification related to the etiology of the disease.
The main types of conjunctivitis depending on the cause of the inflammatory process:
- bacterial (angular, purulent, papillary, gonococcal, diphtheria, gonorrheal, pneumococcal);
- chlamydial;
- viral (herpesvirus, adenovirus, catarrhal);
- allergic;
- fungal (candidiasis, coccidosis);
- traumatic (chemical, thermal, cold).
Types of conjunctivitis depending on the morphology of the conjunctiva and the nature of the symptoms:
- purulent – purulent discharge is formed;
- catarrhal - abundant mucus is formed, there is no pus;
- papillary (appears as a manifestation of allergies) – compactions in the form of small grains form on the mucous membrane of the upper eyelid;
- follicular (develops according to type 1 allergic reaction) – follicles form on the mucous membrane of the eye;
- hemorrhagic – hemorrhages form on the mucous membrane of the eye;
- membranous - develops against the background of ARVI.
To determine the exact type of disease, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination. Without diagnostics, it is difficult to select local drugs that should be effective against certain viruses, bacteria or fungi.
Causes
Types of disease depending on the cause of inflammation:
- Bacterial - caused by pathogenic microorganisms (streptococci, gonococci, diphtheria bacilli, etc.).
- Chlamydial - occurs when chlamydia enters the conjunctival sac.
- Angular - develops under the influence of diplobacillus. It is also called angular conjunctivitis.
- Fungal – manifests itself as a result of the proliferation of pathogenic fungi.
- Viral – caused by a variety of viruses (herpes virus, adenovirus).
- Allergic conjunctivitis - develops under the influence of an allergic factor.
- Dystrophic - occurs under the influence of substances that are aggressive to the mucous membranes of the eyes (paint and varnish material, chemical reagents).
Symptoms
Symptoms of conjunctivitis (see photo) in adults are less pronounced than in children. In childhood and adolescence, catarrhal manifestations are pronounced: redness, swelling of the mucous membrane, clear discharge from the nasal cavity and general weakness. In adolescents and middle-aged children, predominantly viral inflammation of the conjunctiva occurs, which appears a few days after the development of ARVI. In most cases, the body temperature rises.
There are several nonspecific symptoms that are common to all types of conjunctivitis. These include:
- Swelling and redness of the eyelids.
- Swelling of the mucous membrane.
- Redness of the conjunctiva.
- Reaction to light.
- Tearing.
- It hurts in the eyes.
- Sensation of a “mote” in the eye.
- Discharge of pus and/or mucus.
Most often, conjunctivitis is accompanied by a rise in temperature, general weakness, catarrh of the respiratory tract, and so on. Conjunctivitis also manifests itself with specific symptoms, which make it possible to diagnose a specific type of inflammation. To do this, you need to conduct a series of tests.
Specific symptoms of conjunctivitis depending on the type of eye damage:
| Bacterial conjunctivitis | Regardless of the bacterium that triggered the inflammatory process, the primary symptoms are approximately the same - a cloudy, gray-yellow discharge suddenly appears on the mucous membrane, sticking the eyelids together in the morning. Additional symptoms are pain and stinging, dryness of the mucous membrane and skin of the eyelids. Almost always one eye is affected, but if hygiene rules are not followed, the disease spreads to the other. |
| Viral conjunctivitis | The main symptoms are severe redness of the eyelids and mucous membrane of the eye, infiltrates and follicles on the mucous membrane, and the formation of easily removable films. Additionally, blepharospasm, lacrimation, and photophobia are observed. |
| Chlamydial conjunctivitis | The onset of the disease is acute, its main symptoms are severe photophobia, accompanied by rapid redness and swelling of the mucous membrane. During the night, the eyelids stick together with a small amount of mucopurulent discharge. The lower eyelid is most affected. The disease begins in only one eye, but with poor hygiene it spreads to both eyes. |
| Allergic conjunctivitis | Symptoms are severe itching and burning of the eyelids and mucous membranes of the eyes, severe swelling and redness, lacrimation and photophobia. The diagnosis is made as a result of diagnostics and anamnesis, this is important for the effectiveness of treatment. |
| Angular conjunctivitis | This form of conjunctivitis is called “angular” and often becomes chronic. Its appearance is provoked by the Morax-Axenfeld bacterium. Symptoms include pain and itching in the corners of the eyes, which is most severe in the evening. The skin in the corners of the eyes turns red and becomes cracked. A small amount of viscous mucus appears on the reddish mucous membrane of the eye. It accumulates in the corners of the eyes overnight, taking on the appearance of a dense lump. Timely diagnosis and treatment will quickly relieve the symptoms of the disease, otherwise it will become a chronic process. |
Chronic course
Chronic conjunctivitis in adults most often develops against the background of:
- untreated acute form of bacterial, viral, fungal conjunctivitis;
- pathological refractive errors;
- wearing incorrectly fitted lenses;
- chronic diseases of the digestive and endocrine systems;
- trichiasis (improperly growing eyelashes that constantly irritate the mucous membrane of the eye);
- seasonal vitamin deficiencies, etc.
The disease has a wavy course. After the disappearance of symptoms, a period of remission begins, which can last quite a long time (from six months or more). If factors that contribute to the activation of infection begin to act, the inflammatory process begins again.
Complications if left untreated
Late or incorrect treatment can cause a number of complications, which will be much more difficult to cope with.
Complications of conjunctivitis include:
- blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids, accompanied by the formation of phlegmon, trichiasis, scars);
- keratitis (infection of the cornea);
- iridocyclitis (infection inside the eyeball);
- symblepharon (a pathology in which the conjunctiva fuses with the tissue of the eyelids);
- endophthalmitis (purulent inflammation of the eyeball), etc.
There are also borderline forms of pathology, in which damage to the conjunctiva and neighboring tissues is noted. These are primarily blepharoconjunctivitis (accompanied by inflammation of the eyelids) and keratoconjunctivitis (the lesion also affects the cornea).
Infection from the eyes can spread to other organs, in particular, the ears (otitis media develops), the meninges (provokes meningitis). If bacteria enter the bloodstream, sepsis can occur.
The main danger of the disease is damage to the cornea and internal structures of the eye. As a result, vision can deteriorate significantly, up to complete blindness. The pathology is also fraught with inversion of the lower eyelid and the appearance of scars both on the eyelids and on the eyeball. That is why you should not put off visiting a doctor and self-medicate.
How to treat conjunctivitis
The main thing in the treatment of all forms of the disease is to eliminate the cause of the negative symptoms of the inflammatory process. For this purpose, drug therapy is used.
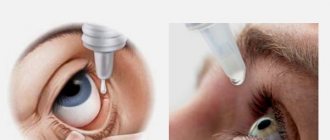
Treatment of conjunctivitis in adults depends on what causes the inflammation of the eye. At the same time, how to treat conjunctivitis at home in adults and children depends on the recommendations of the ophthalmologist. Treatment of eye conjunctivitis at home is carried out using instillation, rinsing, and using ointments.
Pain that appears with the first signs of conjunctivitis is relieved by administering drops of local anesthetics (Lidocaine, Trimecaine, Pyromecaine). Hygienic treatment of the ciliary edge of the eyelids and the mucous membrane of the eye is carried out with antiseptic solutions (Furacillin, Dimexide, Oxycyanate, potassium permanganate, brilliant green).
After relieving pain and hygienic treatment of the eyes, treatment of the cause of the disease begins:
| Bacterial conjunctivitis | Albucid drops, local antibiotics (Levomycetin drops), and ointments are used. This form of the disease develops when microorganisms and bacteria enter the mucous membrane. As a rule, the causative agents are streptococcus, pneumococcus, staphylococcus, chlamydia, gonococcus. If conjunctivitis is one of the symptoms of another disease and is protracted, then treatment includes taking antibiotics and other drugs necessary to treat infections. It is important that purulent conjunctivitis is diagnosed by a doctor and prescribed appropriate treatment in adults and children. |
| Viral conjunctivitis | The causative agents of this form are adenoviruses, herpes, enteroviruses, etc. An inflamed eye is treated in this case with Acyclovir, Zovirax (for an illness caused by herpes). Treatment of redness and inflammation of the eye is also carried out with the drugs Actipol, Trifluridine, Poludan. |
| Allergic conjunctivitis | Diseases of allergic origin are provoked by a variety of irritants - pollen, dust, food, drugs. This form of the disease is manifested by lacrimation, redness, swelling of the eyelids and itching. Such symptoms do not go away for a long time. To cure this disease, it is important to determine which allergen caused this condition and, if possible, limit contact with it. The child should be examined by a pediatric allergist, as more serious manifestations of allergies may develop later. It is the specialist who will tell you how to cure this condition completely. The disease should be treated with Allergodil, Olopatodine, Dexamethasone, Cromohexal, Lecrolin. |
In a similar vein, let's look at how to treat other, less common types of conjunctivitis in adults:
- Gonococcal – Sodium Sulfacyl 20%, Levomycetin, Floxal. It is also recommended to wash the eyes with a weak solution of boric acid and undergo a course of therapy with penicillin-based drugs.
- Enteroviral - eye drops with interferon (Ocoeron, Ophthalmoferon), corticosteroid and antiallergic drugs.
- Pseudomonas - Floxal, Tsipromed, Kolbiitsin and other antibacterial drugs. Additionally, antihistamines are prescribed (Allergodil, Opatanol, Lecrolin).
- Chlamydial - it is recommended to use Erythromycin or Tetracycline ointment (apply behind the lower eyelid 4-5 times a day);
- Fungal - since there are no antifungal eye drops, therapy consists of oral administration of Fluconazole and Intraconazole tablets. Local treatment is carried out using antiseptic drops Okomistin or Vitabact.
What is conjunctivitis? Characteristics of the disease
Ophthalmologists call conjunctivitis an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye, that is, the conjunctiva. Most often, the cause of this disease is an infection, but often this inflammatory process can also be aseptic in nature.
In this article
- What is conjunctivitis? Characteristics of the disease
- Classification
- Causes of infection
- Symptoms and diagnosis of conjunctivitis
- Conjunctivitis in adults. How to treat at home?
- How to cure conjunctivitis?
- Methods Conjunctivitis in adults: treatment with ointments
- Home treatment: what is it like?
- Is it possible to cure conjunctivitis with eye exercises?
- How to treat conjunctivitis at home during pregnancy?
- Is it possible to request sick leave for conjunctivitis?
- Recommendations for the treatment of conjunctivitis in adults
As soon as you realize that you have the first signs of conjunctivitis, which we will discuss below, immediately consult a doctor, as starting the process can lead to a worsening of the disease. So why does the disease occur? The thing is that the mucous membrane of the eye performs a protective function, which means it is most often exposed to adverse external factors, including injuries and infections. When the conjunctiva is damaged or contacted by bacteria and other infectious agents, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed due to allergies. As soon as conjunctivitis appears in one eye, after a while the second eye becomes infected, since the infection tends to spread quickly. As for the symptoms, they are often approximately the same for all types of conjunctivitis:
- swelling;
- purulent discharge from the eye;
- itching;
- burning.
But this symptom may also be accompanied by others, depending on the cause of infection, for example, scarring, perforation of the cornea. Often conjunctivitis is accompanied by other inflammatory eye diseases - keratitis, blepharitis, dry eye syndrome.
Folk remedies for the treatment of conjunctivitis
Traditional recipes help to quickly cope with inflammation, especially during pregnancy, when it is not always possible to treat with medications. The first thing to do when the primary symptoms of the disease occur is to wash your eyes. If you don’t have anything on hand, you can use any tea bags.
If the symptoms do not disappear quickly, then try treating conjunctivitis with folk remedies:
- Infusion of blue cornflower and black elderberry. Each component is taken in an amount of 5 grams, placed in a glass of boiling water and left to infuse for 2 hours. After filtering, add tincture of Datura fruit (15 drops) to the product and use the medicine for rinsing and instillation. The result is guaranteed even with purulent inflammation and a developing cataract.
- Honey. The bee product is recommended as a replacement for drops, but only in diluted form (proportion 1:5 with water).
- Warm milk. Ideally, it is recommended to use a steamed goat product due to its bactericidal properties. Procedure options: rinsing, instillation.
- Freshly brewed tea. Both green and black varieties are suitable. Use the liquid for rinsing and lotions, treating the eyes 3-4 times a day.
- Chamomile infusion. Infuse a teaspoon of herbs in a glass of boiling water, filter and use in the same way as the previous option.
- Dill juice. It should only be fresh. Application – as lotions. Sessions are repeated at least 4 times a day. If a purulent process is diagnosed, you can prepare an infusion of the plant’s seeds.
- Rose hip tea. Pre-chopped fruits in the amount of 2 teaspoons are poured into 200 ml of water and boiled for 5 minutes. After complete cooling, the product is filtered and compresses are made using cotton pads.
- Potato. The product is suitable for treatment only in its raw form. The peeled tuber is grated, the white of one chicken egg is added, kneaded well and the finished mixture is placed on cheesecloth. The duration of the lotion is no more than 20 minutes.
- Aloe. The plant is used to treat the eyes for allergic conjunctivitis in adults and children. If there is a viral form, the priority is chamomile or soda, which have antiseptic properties.
If the above folk remedies do not bring the desired result after several procedures and the symptoms only intensify, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. Delay is fraught not only with worsening the clinical picture, but also with a number of complications.
Folk recipes
Folk remedies are popular among pregnant women and small children, because contraindications and side effects are kept to a minimum. Sometimes when using folk remedies, short-term burning of the eyes, lacrimation, and a feeling of sand in the eyes appear. Symptoms go away after blinking. If they persist, cancel the procedures immediately. An allergic reaction is possible.
For conjunctivitis, treatment with folk remedies helps relieve redness of the mucous membrane and reduces swelling. Herbal ingredients are suitable for home therapy. Traditional methods of treating conjunctivitis at home include washing, rubbing the eyes, applying lotions, compresses, and instillation.
Washing and rubbing the eyes with herbal decoctions during home treatment helps remove accumulated secretions from under the eyelids. This will reduce the content of infectious agents and remove the smallest particles of dust.
Compresses and lotions have a soothing, anti-edematous effect. Instilling drops allows the active substance to remain in the visual organ longer.
For home use it is allowed to use:
Chamomile
Chamomile infusion for conjunctivitis. Homemade recipe: 1 tsp. Brew (or a bag) chamomile with boiling water, let it brew. Cool. Apply lotions up to 4 times a day. Can be used for rinsing or instilling drops.
Additionally, we invite you to watch a video with recipes from chamomile and marshmallow:
Welding
Black or green tea without flavorings is brewed with boiling water. Strain from the leaves. Wipe the eyelids no more than 5 times per day. A simple and affordable home method is to apply tea bags to closed eyelids. Rubbing your eyes with tea at home for conjunctivitis is allowed even during pregnancy and in infants.
Dill
Before use, dill should be soaked in a container of water, then rinsed thoroughly under the tap. The recipe is simple: squeeze the juice from dill, apply a generously moistened napkin or cotton pad, and apply to closed eyelids for 15 minutes.
For purulent conjunctivitis, lotions made from dill seed infusion will help. Recipe: brew 1 tsp. seeds in a glass of boiling water.
Rose hip
Boil 2 tsp over low heat. chopped rose hips. Let it sit for half an hour. Rinse your eyesight 4-5 times a day. Home rinsing with rosehip infusion is effective for adenoviral inflammation.
Lavrushka
Infuse 3 bay leaves for half an hour. An infusion of bay leaves for conjunctivitis in children is used for home rinsing, and in adults for lotions. There is no data on the safety of using bay leaves for the fetus in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
Propolis
To prepare the medicine at home, take 5 g of propolis and knead until smooth. The resulting mass is stirred in half a glass of water and left for 2 hours. After straining, instill 2 drops to 3 drops per day.
Honey
Dilute honey and boiled water in a 1:2 ratio, stir well. Apply napkins moistened with honey water as eye lotions.
Potato
Grate raw potatoes on a fine grater. Mix the gruel with egg white. Wrap the resulting mass in a gauze cloth and use it as a compress. Frequency: 2 times per day for 15 minutes. Potatoes are an affordable remedy for home use and are good for relieving puffiness of the eyelids.
Plant juices
For allergic conjunctivitis, aloe (agagave) and Kalanchoe are effective. Parsley, carrots, green salad, celery, and cucumber will help relieve swelling and fill the body with vitamins.
- Aloe for conjunctivitis is used for instillation. The juice of fleshy aloe leaves is diluted with water, proportion 1:10. Apply the resulting solution to the eyes, 2 drops 1 time per day.
- Wipe your eyelids with Kalanchoe juice up to 5 times a day.
- Dilute agave with water 1:10 and instill 2 drops.
- Dilute cucumber juice with water and soda, the required proportion is 3:1:1. Apply as a lotion for 5 minutes 3 times a day.
- Drink a mixture of carrot juice, parsley juice, lettuce leaves, celery (4:1:1:1) or a mixture of parsley juice and carrot juice (1:3) before meals 20 minutes 3 times a day.
Althea
Method of preparation: marshmallow root is infused in chilled boiled water for 8 hours. Marshmallow rinses and lotions are effective.
You will find the golden mustache recipe in the following video:
Video about calendula treatment below:
Medicines for conjunctivitis
If you do not use medication, getting rid of inflammation will be a long process. For effective treatment, the following eye drops should be used for conjunctivitis:
| Name | Characteristic |
| Albucid | Antibacterial drops with bacteriostatic effect. Effective in the fight against staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci, chlamydia, and E. coli. |
| Tobrex | A painless hypoallergenic antibiotic that affects a wide range of pathogens. |
| Oftalmoferon | Used to treat adults and children with viral eye infections. Combines well with other antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents. |
Is it possible to wash your eyes with tea for conjunctivitis?
Conjunctivitis can be viral, bacterial and allergic. Most often the cause of the pathology is infection. Tea bags are permitted.
The tannins contained in it help in the fight against the disease. The main thing is not to use tea leaves with fillers, and let it steep for at least 2 hours before use.
If after two days there is no improvement, tea leaves alone are not enough; complex treatment is required, including medication.
Eye drops for conjunctivitis
Eye drops are the main treatment for eye diseases, including all types of conjunctivitis. Antibacterial drugs are also used to treat conjunctivitis, it depends on the cause of the disease - for bacterial conjunctivitis, drops such as Floxal, Ciprofloxacin, etc. are used.
To enhance the effect, you can put antibacterial ointments behind your eyelids: Floxal eye ointment, Tetracycline ointment.
For allergies, antihistamine drops Opatanol; Lecrolin, etc. are used, as well as hormonal drops and ointments (Hydrocortisone eye ointment, Dexamethasone).
If the cause of the disease is a virus, drugs containing interferon (Ophthalmoferon, Poludan) are prescribed. Often the infection is mixed or the causative agent of the disease cannot be accurately identified during examination; in this case, a set of drops is prescribed.
As already mentioned, the nature of the disease (viral, bacterial or allergic) can only be determined by an ophthalmologist during an in-person examination. He prescribes the final treatment regimen (if necessary, adjust it), but self-medication can lead to the development of complications or the disease becoming chronic. Therefore, if you find signs of conjunctivitis, we recommend that you contact a specialized institution, where highly qualified specialists will help you quickly and effectively cure the disease.
Principles of treatment at home
Treatment of conjunctivitis depends on what exactly causes the inflammation of the eye. At the same time, how to treat conjunctivitis at home in adults and children depends on the doctor’s recommendations. Treatment of eye conjunctivitis at home is carried out using instillation, rinsing, and using ointments. Your doctor will recommend how to cure conjunctivitis quickly, since using exclusively folk remedies is often ineffective. How to treat conjunctivitis depends, first of all, on its type. Therefore, it is necessary to take into account all the differences between the different types of this disease.
Bacterial
During the entire course of treatment, Diclofenac should be instilled into the eyes 2–4 times a day to reduce the severity of the inflammatory process. The discharge must be removed by washing the eye with antiseptic solutions, for example, Furacilin diluted 1: 1000 or 2% boric acid. To destroy the pathogenic microbe, ointments or drops with antibiotics or sulfonamides are used, such as Tetracycline, Gentamicin, Erythromycin, Lomefloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Albucid, etc. Ointment or drops with antibiotics should be administered 4 - 6 times a day, then 2 - 3 times a day until the clinical symptoms completely disappear. Along with antibacterial ointments and drops, Picloxidine can be instilled into the eyes 3 times a day.
Viral
For adenoviral conjunctivitis, interferon preparations, such as Interferon or Laferon, are used to destroy the virus. Interferons are used in the form of instillation of a freshly prepared solution into the eye. In the first 2–3 days, interferons are injected into the eyes 6–8 times a day, then 4–5 times a day until the symptoms disappear completely. In addition, ointments with an antiviral effect, such as Tebrofenovaya, Florenalovaya or Bonaftonovaya, are applied 2-4 times a day. In case of severe inflammation of the eye, it is recommended to inject Diclofenac into the eye 3-4 times a day. In order to prevent dry eye syndrome, artificial tear substitutes are used throughout the course of treatment, for example, Oftagel, Systane, Vidisik, etc.
Herpes viral
In order to destroy the virus, interferon solutions are also used, which are prepared from lyophilized powder immediately before injection into the eye. For the first 2–3 days, interferon solutions are administered 6–8 times a day, then 4–5 times a day until the symptoms disappear completely. To reduce inflammation, relieve pain, itching and burning, Diclofenac is injected into the eye. To prevent bacterial complications in herpetic conjunctivitis, Picloxidine or a solution of silver nitrate is injected into the eyes 3 to 4 times a day.
Chlamydial
Since chlamydia are intracellular microorganisms, treatment of the infectious and inflammatory process provoked by them requires the use of systemic medications. Therefore, for chlamydial conjunctivitis, it is necessary to take Levofloxacin 1 tablet per day for a week.
At the same time, local medications with antibiotics, such as Erythromycin ointment or Lomefloxacin drops, should be injected into the affected eye 4 to 5 times a day. The ointment and drops must be used continuously from 3 weeks to 3 months, until the clinical symptoms completely disappear. To reduce the inflammatory reaction, Diclofenac is administered into the eye 2 times a day, also for 1 to 3 months. If Diclofenac does not help stop inflammation, then it is replaced with Dexamethasone, which is also administered 2 times a day. To prevent dry eye syndrome, it is necessary to use artificial tear preparations daily, such as Oxial, Oftagel, etc.
Allergic
For the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis, local antihistamines (Spersallerg, Allergoftal) and agents that reduce mast cell degranulation (Lecrolin 2%, Kusikrom 4%, Alomide 1%) are used. These drugs are administered into the eyes 2 times a day for a long time. If these drugs do not completely relieve the symptoms of conjunctivitis, then anti-inflammatory drops Diclofenac, Dexalox, Maxidex, etc. are added to them. For severe allergic conjunctivitis, eye drops containing corticosteroids and antibiotics are used, for example, Maxitrol, Tobradex, etc.
Purulent
In case of purulent conjunctivitis, be sure to rinse the eye with antiseptic solutions (2% boric acid, Furacilin, potassium permanganate, etc.) to remove copious discharge. Eye rinsing is done as needed. Treatment of conjunctivitis consists of injecting Erythromycin, Tetracycline or Gentamicin ointment or Lomefloxacin into the eye 2 to 3 times a day until clinical symptoms completely disappear. In case of severe swelling, Diclofenac is injected into the eye to relieve it.
Chronic
For successful treatment of chronic conjunctivitis, the cause of inflammation must be eliminated. To stop the inflammatory process, a 0.25 - 0.5% solution of zinc sulfate with a 1% solution of resorcinol is instilled into the eyes. In addition, solutions of Protargol and Collargol can be injected into the eyes 2 to 3 times a day. Before going to bed, apply yellow mercury ointment to the eyes.
Prevention
It is important to prevent re-infection of the conjunctiva, otherwise the likelihood of an acute process becoming chronic increases. To do this, it is enough to follow these rules:
- Strengthen the body's defenses.
- Normalize the diet, enrich it with foods containing vitamin A.
- Treat infectious diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx in a timely manner.
- Follow the recommendations for caring for contact lenses and glasses.
- Avoid contact with allergens if you are prone to frequent allergic conjunctivitis; during the season of exacerbation of the disease, use medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Avoid touching your face and eyes during the day; change lenses after disinfecting your hands.
- Ventilate the room.
- Change bedding regularly.
- Wash only with boiled water.
- Wash children's toys with soap.
To avoid spreading the infection to other family members, you should use only your own toiletries and bedding.
Viral conjunctivitis: symptoms and treatment in adults Glaucoma: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention Cataract: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention Otitis media in adults: symptoms and treatment, what antibiotics to take?
Traditional methods of therapy
If you have conjunctivitis, tea leaves will help you quickly cope with unpleasant symptoms at home. You should rub your eyes with a strong infusion of black or green tea several times a day. Also, in the acute course of the disease, the following folk remedies are used:
- Chamomile has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. For infusion 2 tsp. dry raw materials are poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water. When the product has cooled, it needs to be strained. Chamomile is used to wash the eyes several times a day.
- Chop the dill, place in a gauze bag and squeeze. The resulting juice is used for compresses on the eyes.
- Crush 10 g of plantain seeds and brew 1/5 liter of boiling water. The eyes are washed with the strained infusion and lotions are made.
- Grind the dope leaves. Brew 30 g of raw materials with 1/5 liter of boiling water, leave for 0.5 hours, strain. The product is used for lotions.
- Bay leaves for conjunctivitis are used to wash the eyes, as lotions and internally. To do this, you need to steep 3 crushed leaves in a glass of boiling water for half an hour.
- Hydrogen peroxide has an antiseptic effect for conjunctivitis. Rub the eyes with a 0.5% solution 2-3 times a day for a week.
- For conjunctivitis, boric acid is used to wash the eyes. To do this, 5 g of powder is dissolved in 300 ml of distilled or boiled water.
Note:
Blueberries are very good for vision. Eating dry or fresh berries will help speed up recovery. It is recommended to eat no more than 1 tbsp per day. l., otherwise constipation may occur.
Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis with folk remedies at home
For allergic conjunctivitis, treatment should be carefully selected so as not to aggravate the condition. Components with antihistamine action are used to eliminate swelling and redness. Decoctions of medicinal herbs for allergic conjunctivitis, which are drunk and applied topically, have a good effect. The following recipes are used:
- Mix fragrant violet with celandine in a ratio of 2:3. Pour 5 g of the mixture into a liter of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Once a day you should drink 100 g of infusion. The product is also used for compresses and eye rinsing.
- 1 tsp. barberry leaves pour 400 ml of water and simmer for half an hour over low heat. Strain the cooled broth and rinse your eyes with it every morning and evening.
- It is recommended to instill 2-3 drops of aloe juice before bedtime. Aloe decoction is also used for allergic conjunctivitis. Cut one leaf of the plant, pour hot water (half a liter) and leave for an hour. The resulting infusion is filtered and used for compresses every 3 hours.
- 1 tbsp. l. Pour boiling water (300 ml) over eyebright and leave on low heat for 5 minutes. The strained broth is used for compresses and rinses.
Also, to treat allergic conjunctivitis at home, use chamomile, elderberry flower and fruits, comfrey, cornflowers, and calendula.
Read in a separate article: Follicular conjunctivitis: treatment in adults and children
Application of bee products
Honey, propolis, and pollen are used for treatment. These folk remedies are especially useful for chronic infectious conjunctivitis. Allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva is not recommended to be treated with bee products due to their high allergenicity. The following recipes are used:
- Honey is diluted with boiled water in a ratio of 1:2. The solution is dropped into the eyes or applied as a lotion. The therapeutic course lasts 21 days. If necessary, it is repeated after 10 days.
- Flower pollen is taken orally, 1 tsp. 3 times a day for a month.
- Honey is mixed with fish oil in equal proportions. The resulting mixture is placed behind the lower eyelid overnight for 3 days. Then the procedure is carried out every three days.
- An aqueous solution of propolis will help cure conjunctivitis at home in an adult. The dry powder is poured with warm water in a ratio of 1:4 and filtered through sterile cotton wool. The product should be instilled into the eyes every 3 hours.
Important! Before using any recipe, you need to be sure that there is no allergic reaction to bee products.