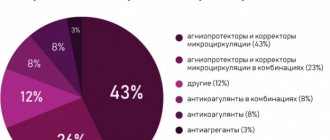
Causes and risk factors of the disease
Colpitis develops as a result of active reproduction of pathogenic flora:
- mushrooms of the genus Candida;
- anaerobic bacteria;
- chlamydia;
- Trichomonas;
- gonococci.
Increase the risk of developing colpitis:
- insufficient personal hygiene;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- refusal of barrier contraception.
The normal microflora of the vagina is suppressed by antibiotics and hormonal drugs.
Signs of vaginitis
Bacterial vaginosis occurs due to a decrease in the number of lactobacilli and an increase in anaerobic flora. The frequency of occurrence is from 16 to 65%. It is characterized by the appearance of copious yellow-gray discharge with a pungent fishy odor. Accompanied by itching and burning in the vagina.
Candidal colpitis, or thrush, is a common infection among women of all ages. It is characterized by intense itching in the vagina and copious cheesy discharge.
Symptoms intensify during water procedures and after sleep. If the infection lasts for a long time, pain occurs during sexual intercourse. Candidal vaginitis is often observed during pregnancy.
Trichomonas colpitis is caused by vaginal Trichomonas. The infection is transmitted sexually. Characterized by copious foamy discharge. A woman experiences pain during urination and sexual intercourse.
Aerobic colpitis is caused by staphylococci, streptococci, and Escherichia coli. Accompanied by itching, burning, profuse yellow discharge. Often becomes chronic.
Gonococcal colpitis is associated with infection with gonococci. The bacterium is transmitted through sexual contact. Accompanied by burning, pain during urination and sexual intercourse. The discharge is abundant, yellow-green in color.
Age-related colpitis develops in menopausal women and is associated with a decrease in estrogen levels. It is also called atrophic, since the vaginal mucosa becomes thinner and mucus production decreases. Accompanied by vaginal itching, dryness and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Symptoms of vaginitis
The main clinical signs of the disease are:
- burning and itching in the reproductive organs;
- the appearance of copious discharge from the genital organs, which can be mucous, bloody, purulent, cheesy, foamy (with senile vaginitis, when atrophy of the mucous membrane occurs, there is no discharge);
- swelling and redness of the external genitalia;
- increased body temperature;
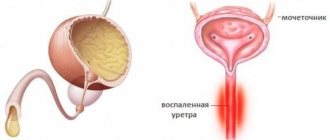
- frequent urination;
- periodic aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during intercourse.
The severity of the above symptoms depends on the form, acute or chronic, of vaginitis, as well as on the type of pathogen, the age of the patient, and the individual characteristics of her body.
In acute vaginitis, the clinical picture is clear . With the candidiasis form of the disease, the patient is bothered by copious curdled discharge, burning and itching in the genital area. With nonspecific vaginitis, the predominant symptoms are profuse foul-smelling discharge and itching in the vagina.
If the inflammation is severe, then an increase in body temperature is observed, and small pinpoint foci of ulceration may appear on the vaginal mucosa. If you scratch them, bloody discharge may appear; in addition, a secondary infection may occur, which worsens the prognosis of the disease.
Chronic vaginitis occurs in an erased form, the symptoms are mild, which makes it difficult to diagnose. There is little discharge, there is almost no swelling and redness of the genitals. Pain and fever are usually also absent. The main symptom of chronic vaginitis is constant itching in the genital area, which intensifies during menstruation, after sexual intercourse, and when walking.
Diagnosis of vaginitis
The diagnosis is made during a gynecological examination. The vaginal mucosa is red and congested. There is copious discharge on the walls. The exception is atrophic colpitis, in which the mucous membrane is pale and blood vessels are visible through it. There is little mucus on the walls. Features of different vaginitis can be seen in the photo.
To determine the cause of the disease, a smear is taken from the vaginal walls. It is examined under a microscope and cultured on nutrient media. This is how the microorganism that caused the inflammation is determined.
Treatment of vaginitis
Treatment of colpitis is carried out with drugs in suppositories and tablets. They are selected taking into account the established reason:
- for candidiasis infection - antifungal drugs;
- for bacterial infection - antibiotics;
- for age-related changes - hormone replacement therapy.
Treatment of bacterial vaginitis is carried out with suppositories containing metronidazole. Then suppositories with lactobacilli are prescribed, which restore the normal microflora of the vagina.
Additionally, bacterial vaginitis is treated with sitz baths with chamomile infusion.
For candidal inflammation, fluconazole preparations are prescribed orally or in suppositories. After this, suppositories with lactobacilli are used.
Gonococcal and trichomonas infections are treated with antibiotics of the penicillin group. At the same time, probiotics are prescribed orally and in suppositories.
Treatment of age-related colpitis in women is complex. The gynecologist selects hormone replacement therapy that maintains sufficient estrogen levels. Since little mucus is produced, local moisturizers - gels, sprays - are added to the treatment of atrophic colpitis.
Effective treatment of colpitis symptoms in women is complex. It is necessary not only to influence the cause of inflammation, but also to eliminate the changes that have arisen in the vaginal wall. To do this, use sitz baths with a decoction of chamomile or sage, tampons with sea buckthorn oil or panthenol.
Treatment of vaginitis with folk remedies at home
Non-traditional methods of therapy involve the use of a large number of different methods and techniques aimed at relieving inflammation in the vulva, eliminating the pathological focus of infectious inflammation and stimulating a more accelerated process of regeneration of epithelial cells that were destroyed by the acute development of the disease. Among the abundance of folk recipes, the following remedies are most often used in treatment, as well as those that have proven their effectiveness in the course of their practical application.
Herbs
Based on medicinal herbs (chamomile, coltsfoot, St. John's wort, sage, thyme), various decoctions are prepared, which are used internally as anti-inflammatory teas, or the vaginal cavity is douched using a healing liquid. To prepare this kind of home medicine, you need to take at least 15 grams of dry leaves and stems of a medicinal plant from the list above, pour them into a metal container, add 1 liter of running water and boil over low heat for 20 minutes.
Upon completion of the preparation process, the woman receives a full-fledged therapeutic product, which must cool to a temperature of 35-40 degrees Celsius. Once the specified temperature indicators are reached, the decoction is ready for use. The treatment method involves the woman taking a rubber bulb full of herbal extract and injecting it into her vagina.
The procedure is recommended to be carried out in the morning and evening after preliminary water procedures.
In this case, the patient should be in a supine position to prevent leakage of the medicine and ensure the longest possible retention of the decoction inside the vagina.
This will ensure positive therapeutic contact of the inflamed mucosa with the biochemical components present in the herbal mixture. The approximate course of therapy is from 10 to 15 days. This lasts longer than when using antibacterial drugs with a chemical formula, but there are no side effects from herbal decoctions, synthetic components do not penetrate into the blood and they do not upset the bacterial balance in the intestines and directly in the vagina itself. This treatment method is excellent for women who are prone to allergic reactions to pharmaceutical medications.
Oils
Essential oils of eucalyptus, mint, sea buckthorn, and rose hips are used as this medicine, which contain the maximum concentrate of all useful substances found in a particular type of medicinal plant. It is practically impossible to prepare medicinal oil at home, because it will still not be possible to comply with the stipulated technological requirements. It is better to buy a ready-made essential extract at the pharmacy. The treatment consists of taking a small amount of oil on the tufts of the index and middle fingers and lubricating the inner walls of the vagina with it.
The anti-inflammatory agent is applied evenly over the entire mucous membrane of the inflamed organ. Already 3-5 days from the start of therapy, the first signs of positive dynamics towards recovery appear. The severity of the inflammatory process decreases, swelling of the epithelial tissues goes away, and the feeling of pain, burning and itching inside the vulva disappears. It is best to use essential oils as part of complex therapy in order to achieve the most positive results at all stages of treatment.
Conspiracies
Traditional medicine is famous not only for the active use of the gifts of nature, but also uses the power of the prayer word in the fight against vaginitis. In this case, conspiracies are used that have helped women get rid of the disease for many centuries, and the sacrament of ritual prayer has been passed down from generation to generation, preserving the tradition of treating vaginitis with the help of conspiracies. In order to apply this type of therapy, you should contact a woman who is engaged in this kind of healing.
In rural areas they are called “grandmothers”, “whisperers”, “witches”. These traditional healers by nature have a strong energy field and every prayer word spoken from their lips acquires enormous potential for materialization. The healer reads a prayer, charms the water and gives the woman methodological instructions on how to properly undergo treatment, how to use charged water, what to do, and what actions it is better to refrain from.
Complications of vaginitis
Vaginitis is dangerous for pregnant women and women planning pregnancy. At the stage of pregnancy planning, colpitis reduces the likelihood of conception. In the first trimester of pregnancy, the risk of miscarriage increases. In the second trimester, the risk of premature birth and the development of intrauterine infection remains. In the later stages, inflammation contributes to the development of postpartum complications - endometritis, salpingoophoritis.
In the absence of timely treatment, the disease becomes chronic. This contributes to the spread of infection to the uterus, tubes and ovaries. Inflammation of the pelvic organs leads to the development of adhesions.
Constantly inflamed mucous membranes may undergo atypical changes. This is a background process for the occurrence of malignant tumors.
Prevention of vaginitis
Help prevent vaginal inflammation:
- careful adherence to personal hygiene;
- limiting the number of sexual partners;
- use of barrier contraception;
- healthy lifestyle - giving up bad habits, balanced nutrition, good sleep.
If you experience heavy discharge with an unpleasant odor, you should immediately consult a doctor. This is the first symptom indicating the development of colpitis.
Inflammation of the vagina is caused by opportunistic or pathogenic flora - bacteria, fungi. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of copious, unpleasant-smelling discharge. The woman is bothered by itching, pain during urination, and sexual intercourse. Vaginitis is most dangerous for pregnant women. Treatment is carried out comprehensively, taking into account the identified microflora.
Womenfirst
- Murtazin A.I. Obstetrics and gynecology. Standards of medical care. Quality assessment criteria. Formulary. 2020 (electronic version)
- Gynecology: national guide / ed. G.M. Savelyeva, G.T. Sukhikh, V.N. Serova, I.B. Manukhin, V.E. Radzinsky.-2nd ed., revised. and additional - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2021. - 1048 p.
- Acute vaginitis of mixed etiology: a modern approach to treatment Malova Irina Olegovna, Afanasyeva Irina Gennadievna, Gusevskaya Ksenia Alekseevna 2021 / Obstetrics and gynecology: News. Opinions. Training
- Modern possibilities for treating vaginitis in pregnant women I. L. Kopobaeva, N. G. Gazaryan 2021 / Medicine and ecology
- AGE-ASSOCIATED FEATURES OF RESTORATION AND MAINTENANCE OF VAGINAL MICROBIOTA IN THE TREATMENT OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF THE FEMALE GENITAL ORGANS Dobrokhotova Yu.E., Ozolinya L.A., Bondarenko K.R., Lapina I.A., Dvornikov A.S. 2021 / Gynecology
RUS2132959 from 03/27/2020
Vulvovaginitis: official and folk treatment, quick healing!
Women's diseases are quite successfully treated comprehensively, that is, both with official doctor's prescriptions and with traditional medicine methods, in particular, herbal medicine.
Vulvovaginitis
– inflammation of the vagina and external genitalia (labia majora and minora, clitoris, vestibule of the vagina).
The development of the disease is facilitated by non-compliance with personal hygiene rules, insufficient ovarian function, and common chronic diseases. The causative agents of the inflammatory process are a variety of microorganisms (staphylococci and streptococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, fungi, viruses, etc.). Depending on the cause of the disease, there are:
• specific vulvovaginitis caused by a specific infectious agent (gardnerellosis, genital herpes, gonorrhea, candidiasis, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia);
• nonspecific vulvovaginitis caused by “common” microorganisms (bacterial vaginitis) or general diseases.
Symptoms
• Discharge (leucorrhoea).
By the appearance of the discharge, one can presumably determine the type of infectious agent. Thus, with thrush (candidiasis), caused by a fungus, abundant white discharge with flakes similar to cottage cheese (“curdled discharge”) is observed. With gardnerellosis, the discharge is clear and has an unpleasant odor (similar to fishy). Thick white-yellow or yellow-green (purulent) discharge is characteristic of coccal microflora (including gonorrhea).
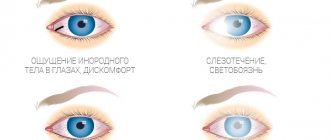
• Itching, redness and swelling of the skin of the external genitalia.
• Burning sensation when urinating.
• Pain during sexual intercourse.
When to see a doctor?
Any vulvovaginitis requires mandatory treatment even if it does not cause severe inconvenience, since the spread of infection inside (into the uterus, fallopian tubes, appendages) can cause chronic inflammation, which is difficult to treat and often leads to infertility.
Medical appointments
SURVEY
This is interesting:
Rules of barbecue: eat and stay healthy. How not to poison yourself and your children with fried smoke and meat
Leucorrhoea, itching, redness and swelling of the skin of the external genitalia occur not only with vulvovaginitis, but also with many other inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs (cervicitis, endometritis, etc.). Therefore, in addition to a general medical and gynecological examination and routine tests, additional methods are used to make a diagnosis:
• ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
• bacteriological and cytological examination of smears from the vulva, vagina, urethra and cervix;
• when a pathogen is identified - tests (culture) for sensitivity to antibiotics, etc.
Treatment
Treatment is usually carried out on an outpatient basis (at home). In the acute stage, bed rest, washing the external genitalia 2-3 times a day with a warm solution of antiseptics (potassium permanganate, chamomile infusion, etc.), and antibacterial drugs for local and general use are prescribed.
When identifying a specific
Vulvovaginitis requires simultaneous treatment of the sexual partner to prevent relapse. Medicines are prescribed taking into account the data of a bacteriological study of the sensitivity of the pathogen to various antibacterial drugs.
This is interesting:
4 valuable recipes for four serious diseases: should always be in stock
Medications should be used as prescribed by a doctor and under his supervision. Their choice (name, dosage form, etc.) depends on the cause and severity of vulvovaginitis. Antibacterial drugs are most often prescribed for topical use in the form of creams, ointments, vaginal suppositories, and douching solutions.
Antibacterial drugs for topical use
: Aminitrazole (Nitrazole) Ketoconazole (Livarol) Clindamycin (Dalacin, Clindacin) Metronidazole (Trichopol) • Miramistin • Nifurtel (Macmiror) • Povidone-iodine (Betadine, Iodoxide) • Polygynax • Polycresulene (Vagotil) • Chamomile preparations (Romazulan) • Ciclopirox (Batrophen) • Citeal.
Home Remedies
Traditional medicine recipes for internal use
✓ St. John's wort herb - 5 g, common thyme herb - 10 g, coltsfoot leaves - 10 g, stinging nettle leaves - 5 g, buckthorn bark - 5 g, calamus rhizome - 10 g. Pour 2 tbsp. l. mixture with 2 cups of boiling water, leave overnight in a thermos, strain. Take 1/2 cup 3 times a day for acute vaginitis.
✓ Common birch leaves, St. John's wort herb, forest raspberry shoots, peppermint herb, horsetail herb - equally. Pour 5 g of the collection into 250 ml of boiling water, heat in a water bath for 10 minutes, strain. Take warm, 1/2 cup 3 times a day, 20 minutes before meals.
This is interesting:
Arthrosis: a friend got rid of terrible pain and shared how she did it. Simple recipes, but very effective!
Traditional medicine recipes for external use
✓ Blue blackberry leaves – 50 g, pour 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 1 hour, strain. Use the infusion for douching for chronic inflammation of the vagina and leucorrhoea.
✓ Quickly grate the onion; Place the grated mass on a piece of gauze measuring 10 by 10 cm, tie it and place it in the vagina for 8–12 hours (individually). Use for trichomonas inflammation of the vaginal mucosa.
✓ Grate the garlic on a fine grater (or chop the wild garlic), take a piece of gauze measuring 10 by 10 cm, put freshly grated pulp on it, tie it and insert it into the vagina. Leave for 3-4 hours a day, longer if possible. Use for trichomonas vaginitis.
✓ Coltsfoot leaves – 50 g, pour 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 1 hour, strain. Use the infusion for douching for chronic inflammation of the vagina and leucorrhoea.
✓ Chamomile flowers, cinquefoil erecta herb - 5 g each. Pour 1 tbsp. l. mixture with 2 cups of boiling water, leave overnight in a thermos, strain. Use for vaginal douching.
✓ Great plantain herb, chamomile flowers - equally. Pour 2 tbsp. l. mixture 1/2 liter of boiling water, leave for 1 hour. Use morning and evening for douching for leucorrhoea.
source