Sulfur plug - what is it?
A sulfur plug is a dense formation consisting of sebum and sulfur. All these products are produced by the ear glands.
The composition of the cerumen plug includes cells of the desquamated epithelium lining the external auditory canal. It also contains dust particles.
The cork may have different colors. Sometimes it is yellow and sometimes it is dark brown. At first, the cork is soft, and then it becomes dense and can resemble a stone.
Sulfur plugs form in approximately 4% of Russian residents and 6% of residents worldwide. Most often it is found in adults. Ear wax in childhood is a rare occurrence.
Although statistics indicate that this problem is not very common in modern society, doctors say otherwise. In their opinion, the statistics are significantly underestimated. There is evidence that during the course of their lives, almost every person encounters sulfur plugs at least once.
There are several interesting facts regarding earwax that simply cannot be ignored:
- In the Middle Ages, sulfur was used as a lip care product. Ancient manuscripts were also written with it.
- Women's earwax has a higher acidity than men's earwax.
- The composition of this substance differs not only depending on a person’s gender, but also on his race. So, for Asians, sulfur is low-fat and dry, but for African Americans it is soft and contains a lot of fat.
- History itself proves the fact that the ears have the ability to independently cleanse themselves of wax. The situation described happened at the beginning of the twentieth century. One Chinese man had his eardrum damaged by a bamboo sliver. They tried to remove it, but every attempt ended in failure, since the sliver opened up and could completely tear the membrane. Then they left the man alone and decided to just watch him. However, the ear was not inflamed. Over time, the sliver approached the edge of the eardrum, and then came out along the wall of the ear canal. However, there were no signs of damage left in the ear.
Content:
Ear plugs in children and adults, photo
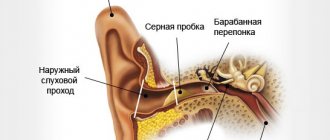
This is what our ear looks like in cross section.
The ear canal is divided into 2 parts :
- Membranous-cartilaginous part located close to the surface
- Bone part , near the eardrum
Between these two parts there is a narrow passage, the most vulnerable place of the ear canal, where sulfur accumulates. The auditory canal is covered with skin and is protected by several glands:
- Sebaceous , with the help of which sebum is produced
- Sulfuric acid , thanks to which sulfur is produced - a milky liquid
- Sweat , responsible for the work of sweat areas
What is sulfur made of?
Sulfur is formed only in the membranous part .
The composition of earwax is rich in different components. Sulfur consists of components:
- Belkov
- Enzymes
- Zhirov
- Immunoglobulin
- Epithelium
- Cholesterol
- Keratin
- Hyaluronic acid
This is interesting . In men and women, sulfur has different chemical composition: in women it is more acidic. Also, sulfur has different composition on different continents of our Earth: Asians have dry sulfur and have more proteins, Africans have more fats.
Why is sulfur formed?
This is what a wax plug in the ear looks like.
Wax is formed in all people . It lubricates the ear canals and protects them from dust, dirt, insects and infections entering the ear.
Read also Adenoids - causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of adenoids
All these foreign bodies, entering the ear, settle on the wax, it thickens and comes out on its own after we talk or chew. And only in some people it cannot come out on its own and accumulates inside the ear canal, creating a plug there.
Each of the components that make up sulfur has its own purpose:
- Fats prevent the skin of the ear from getting wet if water gets into the ear.
- The acidic environment prevents bacteria and fungi from multiplying
This is interesting . Each of us produces 15-20 mg of sulfur per month.
Classification
The color of wax plug can vary from yellow to brown. During the examination, the doctor determines the consistency of the sulfur plug. This is necessary to determine which method to remove the conglomerate - wash or use the dry method. The main criterion for distinguishing types of sulfur plugs is their consistency. The denser the conglomerate, the more difficult it is to extract.
According to this criterion, the following sulfur plugs are distinguished:
- Pasty. They belong to the soft category. They have a color from dark yellow to light yellow. The consistency is soft, moderately fluid, reminiscent of fresh honey.
- Epidermal. The etiology of this type of traffic jam remains unclear. The composition of the conglomerate includes particles of the upper layer of skin (epidermis) and sulfur. The color of the cork is gray, the density is first loose and then rocky. Education often leads to otitis media. According to scientists, such a plug occurs in people with congenital syphilis or with deformities of nails and teeth.
- Plasticine-like. They are also a type of soft plugs. The color of the conglomerate is brown. In terms of viscosity, it resembles pliable plasticine.
- Solid. Their composition includes virtually no water, and the color can vary from dark brown to black.
How does the outer ear work?
The outer ear is represented by the auricle. It is elastic cartilage that is covered with skin. On the side of the conch is the auditory canal. On its sides there are two cartilaginous protrusions.
The external auditory canal originates from the outside of the auricle. Its end point is the eardrum. The auditory canal has a slight curvature and two sections. The first is located closer to the exit and consists of cartilage and membrane, and the second is located next to the eardrum and is represented by bone tissue. An isthmus separates these two passages.
The membranous cartilaginous passage is covered with hairs, and glands are also present in it. Some produce sulfur, others produce fat, and others produce sweat. In just 30 days, the sulfur glands produce about 20 mg of sulfur.
The bony part of the auditory canal does not have glands.
Prevention of wax plugs
Prevention includes:
- Regular hygiene of the ears - they must be washed with soap, being careful not to get water into the ear canal.
- Timely treatment of inflammatory ENT diseases.
- Careful use of cotton swabs: with their help you can clean only the area around the ear canal, avoiding the penetration of the swab into it.
It is not possible to prevent the formation of wax plugs in all cases: if the patient’s ear canal has a special structure or the person has increased secretion of wax from birth, it is impossible to influence these factors. But this does not mean that in this case you do not need to adhere to the preventive recommendations described above: they will slow down the formation of deposits.
What does earwax contain? Why does a person need it?
Sulfur contains fats, cholesterol, wax esters and unsaturated fatty acids. This composition of sulfur does not allow it to dissolve in water, but at the same time it provides lubrication of the dermis lining the ear canal, protecting it from dust and drying out.
Earwax contains antibacterial components, as well as lysozyme. It destroys the wall of microbes. It also contains immunoglobulins, which help maintain local immunity. All these components of sulfur, as well as the acidic environment in the external auditory canal, are reliable protection of the internal structures of the ear from pathogenic flora.
The production of sulfur is a natural process that the body needs to protect itself from external attacks.
How do ears clean themselves of wax?
The external auditory canal communicates with the internal part of the temporomandibular joint. When a person talks or chews food, sulfur moves outward from the eardrum.
The skin lining the ear canal grows as quickly as human nails. As it grows, it pushes ear secretions outward. Thus, sulfur, which is attached to the eardrum, after 2-3 months will independently appear near the exit from the ear canal.
In addition, the auditory tube is covered with small hairs that are constantly in motion. Their vibrations also push earwax out.
However, the self-cleaning mechanism of earwax can sometimes fail, resulting in the formation of a wax plug.
Causes of sulfur plugs
There are the following factors that lead to the formation of ear plugs:
- Violation of hygiene rules.
If a person too often uses cotton swabs to clean the ear canal, or uses sharp objects, such as toothpicks, for this purpose, this will lead to the formation of wax plugs. With such actions, it injures the skin, in response to which the sulfur glands begin to work more actively. Earwax is pushed deep into the passage and compacted. As a result, self-cleaning becomes impossible.
Too rough movements with a cotton swab lead to damage to the cilia of the external auditory canal, so they are no longer able to perform their functions as expected.
- Features of anatomy.
Sometimes a person's ear canal is too narrow or tortuous from birth. This becomes an obstacle to self-cleaning of the ear from wax. Such anatomical features can be either congenital or acquired. The shape of the ear canal may change as a result of injury.
- Increased secretion of earwax.
If the lipid balance in the human body is disturbed, this leads to an increase in the amount of cholesterol in the ear canal. This substance is part of earwax. It becomes more viscous and the process of removing it from the ear becomes more difficult. Metabolic disorders can be a hereditary pathology, or develop against the background of certain diseases, for example, atherosclerosis.
- Inflammation and infectious diseases affecting the external auditory canal.
Any diseases of the outer ear lead to the fact that the sebaceous and sulfur glands activate their work. As a result, the ear simply does not have time to cope with such volumes of wax. In addition, the ear canal narrows due to inflammation and swelling of its tissues. This is a mechanical barrier to the release of sulfur.
During illness, the qualitative composition of earwax changes. There is less lysozyme and immunoglobulins in it, which leads to secondary damage to the ear glands, and the course of inflammation only worsens.
- Wearing a hearing aid.
The hearing aid rubs the skin of the ear canal, in response to which the cerumen glands begin to produce more sulfur. A similar situation can occur with frequent use of headphones. The sulfur secretion is pushed into the deep structures of the passage and compacted. This factor can also trigger the development of inflammation.
- Excessive
hair growth in the ear canal.
When there is too much hair in the ear canal, it will interfere with the normal movement of wax through it. Most often, this problem occurs in older people. - Skin diseases of the external auditory canal.
If the patient suffers from psoriasis or eczema, then the epidermis of the skin of the ear canal exfoliates in excess, mixes with sulfur, thickens and blocks the outlet. Also, against the background of non-infectious inflammation, the work of the sulfur glands increases, which aggravates the problem.
- Working in dusty areas.
If a person works in a mine, mill or other industry where there is a lot of dust, then it will certainly settle in the ear canal and disrupt the functioning of his cilia.
- Entry of a foreign body into the external auditory canal.
If there is any foreign body in the ear canal, the glands will produce more secretion to get rid of it. As a result, a sulfur plug may form. Moreover, for self-cleaning of the passage there will be an obstacle in the form of this foreign object.
- Spending a long time indoors with dry air.
If air humidity drops to 40% or less, the skin of the ear canal will dry out. As a result, a hard sulfur plug will form.
- Age characteristics.
As the body ages, the mechanisms for clearing secretions from the ear deteriorate, and its production increases. An increase in the amount of hair in the ears also contributes to the formation of plugs.
Video: causes of wax plug and treatment methods:
Causes of plug formation in the ear
The reasons for the formation of wax plugs in the ears can be very different.
Wax plugs in the ears can form for the following reasons :
- There is a lot of wax in the ears
- Accumulation of sulfur due to poor release
- Diligently cleaning out wax every day with ear sticks, respectively, wax for its intended purpose - protecting the ear canal is not enough, and its production increases
- Various skin diseases
- Inflammatory diseases of the ears
The accumulation of wax in the ear canal can be:
- Due to the narrow passage
- Due to pushing deep into the wax with ear sticks, when cleaning the ear canal
- Foreign object in the ear
- High dust content in the air
- Because of the hearing aid
- Due to wearing small headphones that are inserted inside the ears
Read also Lacunar tonsillitis - symptoms, causes, treatment and prevention
Symptoms of wax plug
For a long time, a person may not suspect that he has a wax plug in his ear, since it does not show itself in any way. The first signs of its presence may appear only when the ear canal is 70% blocked. If the plug has formed in two ears, then the symptoms will be bilateral.
The following symptoms indicate wax plug:
- Deterioration of hearing, feeling of ear congestion. Earwax gradually accumulates in the ear, so the decrease in hearing acuity will progress all the time.
- Prolonged dry cough, dizziness, nausea, pain and echoes of one’s own speech. These symptoms develop when wax builds up and puts pressure on the eardrum. It contains nerve endings that will be irritated. If these signs are ignored, a person may develop myringitis. This term refers to inflammation of the eardrum. The likelihood of developing otitis media also increases. The ear pain will get worse, especially when you move your jaw. Body temperature may rise, and uncharacteristic discharge may appear from the ear.
- Heart rhythm disturbances, facial paralysis, epilepsy attacks. These symptoms occur when a plug forms in the bony part of the ear and puts severe pressure on the eardrum. After getting rid of the plug, the symptoms will be relieved.
Most often, the first signs indicating the formation of a plug appear after contact with water. It increases in size and moves closer to the eardrum, which causes the appearance of corresponding symptoms.
Types of sulfur plugs
There are several types of sulfur plugs (depending on the stage of development of the pathological process), soft and hard. Soft ones include:
- Pasty - newly formed, soft, yellow in color, easily removed from the ear canal.
- Plasticine ones are brown, more dense, and more difficult to remove than pasty ones.
Types of solid plugs:
- Dry - they appeared a long time ago, have a black tint, the wax has dried out and become very compacted, it is difficult to remove such a formation from the ear.
- Epidermal - dried sulfur also contains a large number of dead epidermal cells; such plugs can be accompanied by the release of pus.
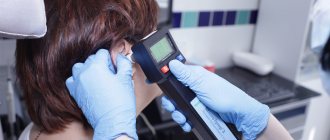
How to remove wax plug from the ear?
To get rid of wax plugs, you can use special means and carry out the procedure at home, or visit a doctor’s office and undergo appropriate therapy.
How to remove wax plug at home?
If the symptoms of the presence of wax plug are quite intense, then this indicates its impressive size. It is not recommended to remove such formations at home, as there is a possibility of infection in the ear. As a result of incompetent actions, a person can damage the skin of the ear canal or eardrum.
Small plugs can be removed from the ear canal yourself, but taking all precautions. It is best to use special preparations for this purpose, rather than cotton swabs.
Can I use cotton swabs?
The deeper a person inserts a cotton swab into the ear canal, the more the wax is compacted. This will cause it to become larger in size and will be more difficult to get rid of.
The stick can damage the skin of the ear canal and even the eardrum itself, so they should not be used.
Drops to dissolve a plug in the ear
To remove wax plugs, you can use special preparations that are sold in pharmacies. They are also used for preventive purposes.
Drops dissolve solid formations and promote their smooth removal from the ear. The procedure for dissolving the plug is called cerumenolysis. During the procedure, the plug does not increase in size, so the person does not experience any discomfort.
Preparations that are used to dissolve cork:
- A-cerumen
, which can be purchased in bottles with a dropper. One bottle contains 2 ml of solution. To remove the plug, you need to drop 1 ml of solution into your ear. After a minute, the passage is cleared. Instillations should be performed once a day for 3-4 days. For prophylactic purposes, the drug is instilled in 1 ml in each passage. The procedure is carried out once every 30 days.
- Remo-vax
, which is available in bottles with a dispenser. The volume of one bottle is 10 ml. To remove the plug, apply 10-20 drops into each ear canal, wait from 20 minutes to an hour, and then perform ear hygiene. The duration of the treatment course is 3-4 days. For prophylactic purposes, the drug is instilled into the ear once every 14 days.
Drops must be used correctly. First, you need to warm them to a comfortable temperature. To do this, hold the bottle with the drug in your palms for several minutes. Or you can heat it up using a water bath. If this is not done, you can cause irritation of the inner ear. It houses the vestibular apparatus, which is responsible for human balance. Therefore, using a cold solution may cause dizziness, vomiting and nausea.
To apply drops, the patient is placed on the side opposite to the sore ear. The drug is instilled along the back or upper wall of the ear canal, but not in its center. After waiting the required amount of time, you need to apply a napkin to your ear and bend over so that the solution flows out. The procedure should be completed by rinsing the ear with saline solution.
It is strictly forbidden to use drops if a person has a damaged eardrum, has been diagnosed with chronic otitis media, or has suffered from purulent otitis media. It is prohibited to use A-cerumen for children under 2 years 6 months.
After the procedure, you must contact an otolaryngologist. The doctor must make sure that the wax plug is completely out of the ear canal.
Video: 5 ways to remove wax plug at home:
The best water-based drops for ear wax
Special water drops are used to safely and painlessly remove wax plugs at home, as well as to prevent its formation. In addition, the ear remedy can be used by a doctor as a preparatory step before removing the ear plug.
A-Cerumen
A-Cerumen are popular and safe drops for dissolving sulfur. The drug is a multifunctional otolaryngological agent for washing the ear canal from wax plugs. According to the instructions for use, surfactants act as active ingredients in the drops. They have a surface-active effect, dissolving sulfur plugs and preventing their re-formation.
A-Cerumen is approved for use in adults and children over 2.5 years old, in pregnant and lactating women. Drops are not recommended for use in the following cases:
- individual intolerance to components;
- perforation of the eardrum;
- acute infectious otitis;
- children's age less than 2.5 years.
Read more How to choose drops for otitis media in children and adults
As a hygienic and prophylactic product, the drug is used 2 times a month, 1 ml in each ear (this dose is equivalent to 1⁄2 bottles). To remove existing blockages, use 1 ml in each external auditory canal 2 times a day. After 60-90 seconds, rinse your ears with boiled water or 0.9% sodium chloride solution. The duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician.
Remo-Wax
Remo-Vax drops are a gentle and safe product for ear hygiene in adults and children from the first day of life. The composition includes a complex of active components that provide a powerful softening and flushing effect on plugs. The preparation contains allantoin, mink oil and liquid lanolin. These substances protect delicate skin from the negative effects of bacteria and have an anti-inflammatory effect. Butylated hydroxytoluene and phenylethanol improve cell regeneration and have an antioxidant effect.
Main contraindications:
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- ongoing inflammatory process in the ear cavity;
- pain in the ear;
- discharge from the ear;
- defects of the eardrum or the presence of a shunt in it.
To dissolve the ear plug, instill 20 drops. To prevent their formation, it is enough to use drops once every 14 days. Remo-Vax is approved for use during pregnancy (1-3 trimester) and lactation.
Aqua Maris Oto
Natural sea water is the main component of the Aqua Maris Oto spray. The drug is recommended for use in adults and children over 4 years of age. Approved for use in pregnant and lactating women. Contraindications:
- the presence of an inflammatory process;
- perforation of the eardrum;
- ear pain (preliminary consultation with a doctor is required).
For hygienic care of the external auditory canal in adults and children, Aqua Maris Oto should be used 1-2 times a day, 2-3 times a week. If there is excessive accumulation of earwax, use the product daily. The duration of treatment is not limited.
Otipax
Otipax drops are a combination drug with anti-inflammatory and local anesthetic effects. The main substances in the drops are phenazone and lidocaine. The last component will reduce the intensity of pain associated with the problem, the first one will inhibit the production of sulfur.
Usually the course of treatment is 10 days. Drops are instilled into the ear 2-3 times a day, 3-4 drops. Children under one year old use 1-2 drops, from 1 to 2 years old - 3 drops, preschool children and schoolchildren - 4 drops 3 times a day. The only restrictions on the use of Otipax are perforation of the eardrum and allergy to the components of the drug.
Otinum
Despite the fact that the main indication for the use of Otinum drops is acute inflammation of the middle ear and otitis externa, it is also used to soften earwax. Most often, doctors use the medication before the procedure for removing a hardened ear plug. To do this, the solution is instilled into the ear, 3-4 drops up to 2 times a day. The duration of use is at least 4 days. Otinum should not be used in the following cases:
- bronchial asthma;
- membrane perforation;
- hypersensitivity to choline salicylate and other components of the drug.
Otinum should not be used by pregnant and lactating women, or children under one year of age. With caution, Otinum drops are used for concomitant polyposis of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, allergic rhinitis (specific inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity).
Hydrogen peroxide to remove wax plug
To remove wax plugs, you can use hydrogen peroxide. It is important that its concentration does not exceed 3%, otherwise it can cause damage to the skin of the ear canal.
After contact with tissues, peroxide begins to disintegrate into oxygen molecules, simultaneously oxidizing the surface affected by it. Foam is formed, which mechanically cleans the passage, freeing it from the plug. Immediately after adding peroxide and getting it on the cork, hearing will deteriorate. This is normal as the cork will swell and increase in size. After ear hygiene is completed, everything will return to normal.
Before applying peroxide into the ear, it must be brought to a temperature of 37 °C. Then the patient lies down on the healthy side and applies 15 drops of peroxide into the passage with the sulfur plug. At this time he will hear a hissing sound. You need to spend 15 minutes in this position, then bend over the napkin and let the liquid flow out. Then the ear is blotted with a cotton swab, but it should not be penetrated into the ear canal itself. To completely remove the plug, you need to carry out the procedure at least four times a day. The duration of the course is from 3 to 5 days. After its completion, all symptoms should be relieved.
To make sure that the plug is completely washed out of the ear, you need to visit an otolaryngologist.
It is prohibited to use hydrogen peroxide if there is a violation of the integrity of the eardrum, or if the person has suffered purulent otitis media. Do not use the drug for chronic otitis.
Peroxide should be used with caution, as it can cause burns to the tissues of the ear canal. Therefore, if during the procedure a person feels pain or a burning sensation, you need to remove the drug from the ear and go to see a doctor.
Oil drops against ear congestion
Preparations in this group promote the gentle removal of sulfur masses without their splitting. They lubricate the ear canal with the oils included in the composition, after which the accumulations of secretions smoothly come out of the ear under the influence of natural mechanisms.
Read more List of ear drops for congestion
Vaxol
The product is made from 100% pharmaceutical olive oil. Vaxol acts as an antimicrobial and antifungal medicine. It effectively relieves inflammation in the ear cavity. The contents of the bottle are designed for 200 uses. To treat wax plugs, the product is used 1 – 2 times a day for 5 days.
Vaxol has a minimum of contraindications - an allergy to olive oil and perforation of the eardrum. The use of the solution in children, the elderly, pregnant and lactating women should be under the supervision of a specialist. Vaxol should only be prescribed to them by a doctor.
Earex
These ear drops can be used to soften and remove hard ear wax, preventing the formation of hardened ear wax. Earex are suitable for adults and children aged two years and older. But before using them to treat a child, you must consult a specialist.
The drops contain only 2 active components - glycerin and hydrogen peroxide. Glycerin softens the sulfur plug, and hydrogen peroxide helps remove it. The product should not be used by people with a damaged eardrum, inflammation of the ear, eczema or allergies to components. For treatment you will need 3-6 drops up to 2 times a day. The duration of use depends on the severity of the problem. But using drops for more than 5 days is not recommended.
Clin Irs
Another popular ear drops. The unique medicine is based on a derivative of olive oil. It contains active chemicals that help effectively solve the problem of ear plugs.
Innovative drops are recommended to be used to soften and dissolve sulfur plugs that clog the ear canals. The therapeutic drug triggers a natural cleansing mechanism. Thanks to this, the patient gets rid of wax seals painlessly. When introducing drops, a gentle flushing method is used, which ensures uniform distribution of liquid throughout the channel.
Rinsing the ear to remove wax plugs
The ear can only be washed in the ENT doctor's office. This procedure is called irrigation. You should not perform such manipulations at home, so as not to damage the integrity of the eardrum.
How is rinsing performed?
If the cork has a soft consistency, then you can wash it immediately. Provided that it is hard, then first you need to soften it. To do this, a person instills 3% concentration of hydrogen peroxide into the ear canal throughout the day. The procedure must be repeated 5-6 times a day. After 3-4 days, the cork will become soft and can be washed out. You can also use pharmaceutical preparations to soften it.
Rinse the ear with saline solution.
The procedure can be carried out using special instruments or devices:
- 100-200 ml of solution is poured into the Janet syringe, which is fed into the ear canal. Under the pressure of the liquid, the particles of the plug come out. The syringe is capable of creating high pressure in the ear (up to 10 atmospheres), and the eardrum can withstand no more than 2 atmospheres. Therefore, the procedure must be performed by a professional.
- The Proplus irrigator allows you to safely and painlessly remove a plug from the ear canal, since the liquid stream is supplied pulsed and under pressure that can be controlled.
If the patient's eardrum is damaged, the procedure is not performed. It is also prohibited for sale provided that the person suffers from chronic otitis or has suffered purulent otitis.
Video: ENT doctor about the dangers of cotton swabs:
How to remove wax plug in the ear at home?
At home, to quickly and effectively remove wax plugs in adults, it is convenient to use special drops designed to dissolve wax secretions. At the pharmacy you can purchase special drops A-Cerumen or Remo-Vax, which have proven themselves in the treatment of this pathological condition. This technique is called cerumenolysis, it is completely safe, does not cause swelling of the conglomerate, which means that the removal of the plug is painless.
A-Cerumen solution is released in 2 ml droppers. To remove the plug, pour 1 ml of solution (1/2 bottle) into the ear canal, wait a minute, then clean it with a cotton swab. The procedure is done twice a day until the sulfur plug comes out. To obtain the desired result, the drug must be used for 3-4 days.
Remo-Vax drops are produced in 10 ml bottles with a plastic dispenser. Place 20 drops of solution into the ear canal, wait 20 minutes, and then clean the ear canal. The procedure must be done daily for 3 days.
To prevent the formation of sulfur plugs, you can use these solutions twice a month. Drops are prohibited for use in case of damage to the eardrum, manifestations of purulent and chronic otitis. A-Cerumen solution should not be used in children under 2.5 years of age.
Rules of application:
- Before the procedure, the drops should be slightly warmed in a water bath or simply hold the bottle with the solution in your hands for 5 minutes.
- During instillation, you need to lie on your side or tilt your head in the direction opposite to the one on which the sore ear is located.
- The solution should be instilled along the upper or back wall of the ear, but not in the center, otherwise an air lock may form.
- After the certain time allotted by the instructions for exposure to the solution, you need to tilt your head so that the remaining medication flows out, then rinse the ear canal with warm water or saline and blot with a clean, dry cloth.
At home, you can use a syringe without a needle or a small pear-shaped enema to rinse the ear canal. If the cork is dry, then before washing it needs to be softened with hydrogen peroxide (3%). To do this, for 3-5 days, before going to bed, place a few drops of the solution in your ear and close the ear canal with a cotton swab.
After instillation of hydrogen peroxide in the ear, a short-term burning sensation and hissing may occur. There is no need to panic about this - this is a completely normal reaction when using the solution. But if the burning sensation does not disappear and causes pain in the ear canal, you need to tilt your head so that the solution flows out of the ear and seek advice from an otolaryngologist.
Once the cork has softened, you can begin rinsing. To do this, stand over the sink, tilt your head to the side and begin pouring water from a syringe into the sore ear, directing the stream along the walls of the ear canal. The procedure can be done twice a day until all symptoms of wax plug disappear.
To remove traffic jams, pharmacy chains offer phytosuppositories with propolis. If desired, you can prepare them at home yourself. To do this, a piece of propolis is softened in a water bath and mixed with a few drops of any essential oil and beeswax. To improve effectiveness, you can add a little decoction of medicinal herbs that have an antiseptic effect.
Ear candles quickly neutralize wax plugs and at the same time have a warming, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect due to a combination of vacuum and gentle heat.
Folk remedies
You can remove the wax plug yourself, but this is only allowed if you are completely sure that the hearing loss is related specifically to this problem and is not accompanied by any concomitant pathology. As mentioned above, in case of decreased hearing acuity, it is necessary to consult a specialist, since only he can reliably make a diagnosis.
There are several folk methods to combat wax plugs, but they should only be used in consultation with your doctor.
- Heat 50 ml of water, dissolve 1 tablespoon of soda and add 3 drops of glycerin, instill 5-6 drops into the ear 4 times a day until the ear is completely cleansed.
- Heat a little milk to about 45 degrees C, add 2-3 drops of hemp oil, drop it into the ear using a pipette 2 times a day.
- Place 3 drops of a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution into the ear at night for an average of 4 days.
- Dilute onion juice with water 1:1, drop into the ear 2-3 times a day for 3-4 days.
Devices for removing wax plugs
As a rule, the otolaryngologist's office has an aspirator and irrigator.
Description of devices for removing wax plugs
| What is the name of the device | Device structure |
| Medical aspirator. It can be stationary or portable. | The equipment of the device includes a container for collecting wax, aspiration tubes, a device for creating a vacuum, and a power regulator. The device is powered from the mains or battery. It also includes a filter that prevents infections from entering the ear. |
| Electronic irrigator. | The device is equipped with a compressor or a knob for adjustment, a foot switch for supplying and stopping water, a pressure and fluid flow regulator, and a hose. The kit includes disposable ear tips, paddles for removing wax, and capes for patients to prevent them from getting their clothes wet. The device is powered from the mains or battery. |
Treatment of wax plug
Removal of wax plugs should only be carried out under the guidance of an experienced otolaryngologist.
Old-timers of the first medical institute remember the case when cerumen was given to the entire staff of the clinic for two weeks! Almost all employees contributed, from interns and subordinates to the head of the department. As a result, the plug was removed. The name of the winner has not been preserved in history.
The method of removing the plug is selected based on the neglect of the process. Soft and pasty wax plugs are removed by routinely flushing the outer ear with warm water under pressure. For this, a syringe without a needle, a syringe, etc. is used.
Dry and hard sulfur plugs require initial softening (using hydrogen peroxide or cerumen) followed by washing.
Plugs that cannot be softened can be removed with a special medical instrument.